cystitis in cats


First, let’s look at the types of this disease.
Contents
Types of cystitis
According to the type of pathology, feline cystitis is divided into:
Acute cystitis
Symptoms of acute cystitis in a cat are characterized by pronounced manifestations: anxiety, blood in the urine, etc. Treatment should be started immediately.
Chronic cystitis
It is characterized by a long course of the disease. Usually, pathological processes in the bladder persist without the manifestation of visible symptoms. If the pet has experienced stress or has a cold in the bladder, the disease will manifest itself again. Thus, chronic cystitis in a cat can periodically worsen.
According to the type of inflammatory process, urocystitis can be divided into:
Hemorrhagic cystitis
Hemorrhagic cystitis is characterized by the presence of blood in the urine of a cat.
Serous catarrhal cystitis
There is mucus in the urine.
Purulent cystitis
In the analysis of urine there is pus. The cat may have white discharge from the urethra.
Feline idiopathic cystitis (FIC)
The trigger is stress, defects in the inner lining of the bladder. In the analysis of urine there are no bacteria and sand.

Causes of cystitis
There are several factors that cause cystitis. From them and the severity of the manifestation of symptoms depends on how to treat cystitis in a cat.
bacteria
Bacterial inflammation of the bladder occurs when pathogenic microflora begins to develop on its wall. Most often, it gets there retrograde, that is, from the urethra. Sometimes the natural microflora, which is conditionally pathogenic (normally does not cause disease), begins to grow due to favorable conditions for it: with too concentrated urine, hypothermia, stress, etc. The number and type of bacteria, their resistance, compliance doctor’s recommendations depend on how long bacterial cystitis in cats will be treated.

Insufficient fluid intake
Cats, before domestication, lived in desert areas. Their body is adapted to conserve water. They rarely feel thirsty and the kidneys concentrate the urine. A high concentration of urine leads to the fact that salts in the urine begin to precipitate, sand and stones (uroliths) form, which irritate the bladder wall and provoke the development of inflammation.

Sedentary lifestyle
In nature, cats constantly hunt. Domesticated Barsiki, although they have not lost their hunting instinct, move much less in an apartment. With high activity, the suspension in the bladder is shaken, does not settle on the walls and is excreted naturally. When the cat sleeps for 10-16 hours, and the food in the bowl does not try to escape from him, the suspension settles on the walls and provokes the development of the disease.
Unbalanced Diet
The diet should be balanced so that the kidneys do not have to excrete excess trace elements in the urine. The development of cystitis is influenced by products that lead to a change in the pH of the urine or contain a large amount of crystal-forming substances. Improper nutrition disrupts the natural environment of the bladder and provokes the development of inflammation.

Urolithiasis (ICD)
This is a pathology in which uroliths form in the urinary system (URS). They have different sizes, shapes and structures. Some types of stones can be dissolved with proper treatment. Some do not dissolve in principle and are only subject to surgical removal.
Urine outflow obstruction
In this regard, males are more susceptible to MVS. In cats, there is a significant narrowing of the urethra (C-bend) in the penis area, so it can become clogged and provoke stasis of urine with the slightest inflammation or the presence of a significant amount of sediment in the urine. Prostate disease also complicates the outflow of urine. Therefore, the treatment of cystitis in a neutered cat is easier than in a stud cat with prostate disease. Is there cystitis with stasis of urine in cats? Of course. But due to the wide urethra, urinary retention in females is much less common.

Stress
Many owners notice signs of cystitis in their pets after a stressful experience. Do cats get cystitis due to the fact that they are worried? Yes. The mechanism of development of FIC is not fully understood, but the most common factor is stress. The reasons for stress are very different: moving, the appearance of a new pet, a trip to the clinic, a new tray, guests in the house, etc. All cats are different, some like to meet guests or drive a car, others hide under the bath from the noise of fireworks. Therefore, this factor in the development of cystitis depends solely on the temperament of the pet.

Defects of the inner lining of the bladder (BM)
The inner wall of the urinary tract may have structural defects, areas of integrity violations, neoplasms, etc. Since urine is a rather aggressive environment, it can irritate the wall of the bladder and provoke the development of cystitis.
Other causes of cystitis
Cystitis as a secondary pathology can cause diseases such as:
Kidney diseases (nephritis, acute and chronic kidney disease, etc.);
Neoplasms (tumors of the bladder or neighboring organs);
Injuries (fall, car injury, blow, bite);
Diabetes;
Viral immunodeficiency of cats;
Poisoning.
In these cases, the underlying disease should be treated, since cystitis in a cat becomes a concomitant disease.
Symptoms of cystitis in a cat
How does cystitis manifest in cats?
Frequent urination (pollakiuria);
Pain when urinating (stranguria);
blood in the urine (hematuria);
Urination in places not intended for this (periuria);
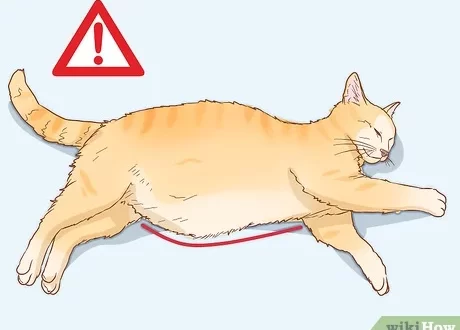
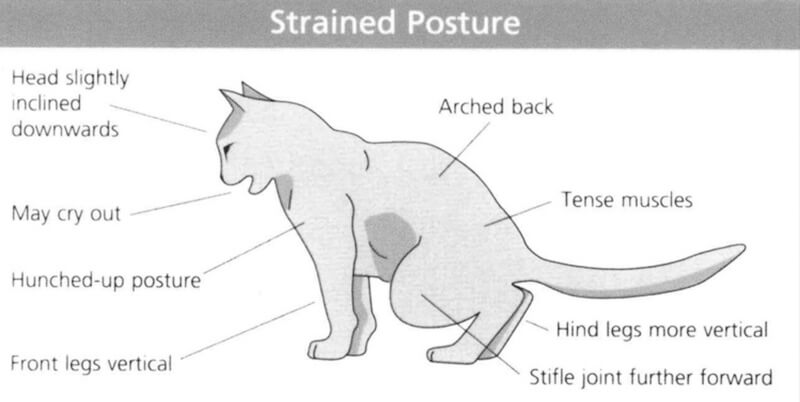
Change in gait and natural postures. Obvious signs: the gait becomes slower, while walking the cat puts its hind legs a little wider, slightly arches the lower back, tightens the pelvis;
Excessive interest in licking the abdomen and perineum;
Abdominal soreness – can be noticed when you take a pet in your arms or try to touch the stomach;
Unsuccessful attempts to urinate – the cat sits on the tray for a long time, pushes, screams, but cannot squeeze out a single drop. This is a very alarming symptom that speaks of a blockage in the urethra. This condition is dangerous for the life of the pet and requires an immediate visit to the doctor;
Vomiting, refusal to eat, lethargy – these signs may be due to a severe manifestation of cystitis or blockage of the urethra. These symptoms require immediate medical attention.
Symptoms of cystitis in cats can be combined with each other, and the treatment in each case will be different. Some signs of cystitis may go away on their own, but reappear over time.

Diagnosis of cystitis
Diagnosis of cystitis requires at least three studies:
Expert review. The doctor will collect a detailed history, conduct an examination: evaluate the condition of the mucous membranes, the size of the bladder, the degree of pain, the presence of edema or pathological discharge in the perineum;
General urine analysis. pH level, density, presence of blood, leukocytes, salts and their type. It is important that you cannot assess the level of protein in a urine test if blood is present in it. After the course of treatment, the analysis will need to be retaken to control the dynamics, then the assessment of the protein level becomes informative. Cystocentesis (puncture through the abdominal wall) is the most informative method of taking a urine sample. This procedure is carried out under ultrasound guidance. Before analysis, the pet must not urinate for 2-4 hours so that the MP is filled. This is a routine procedure that does not require anesthesia, and usually cats respond to it even more calmly than to injections. Urine can also be collected independently. Scrub the tray thoroughly with a chemical-free brush and scald with boiling water. When the pet urinates, collect the urine in a urine container and take it to the laboratory. There are special test tubes with a preservative, in which urine is stored longer. Check with your doctor for the availability of such tubes. An important point: the presence of bacteria in such an analysis does not mean the presence of bacteria in the bladder. They can get into the test tube from the tray itself, from paws, wool or from the urethra. Therefore, we strongly recommend passing a urine test by cystocentesis;
US will help to identify signs of inflammatory processes and their severity, to assess the presence of suspension / sand. In most cases, ultrasound can diagnose the presence of uroliths (stones) or neoplasms. Before the study, it is important that the pet does not urinate for 2-4 hours.
None of these research methods will be sufficiently informative without the other. Only after carrying out all of the above tests, the doctor will be able to say what to give the cat with cystitis.

With disputable results of the main tests or with a long course of the disease without positive dynamics, other studies may be prescribed:
Bacterial culture of urine with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics. It is necessary if the cat, despite treatment, does not get rid of cystitis for a long time, and bacteria are present in the urine. Some bacteria have developed resistance (addiction) to antibiotics. In this case, a urine test is taken by cystocentesis (it is important to take urine directly from the bladder). The sample is sent to the laboratory, where these bacteria are grown on nutrient media and their type and sensitivity to various drugs are identified.
Urethroscopy/cystoscopy. Endoscopic examination method, performed under sedation. Using a special tube with a camera at the end, the urethra and bladder are examined. This is a very informative method, since you can visually evaluate what the mucous membrane looks like. If necessary, during cystoscopy, an analysis can be taken from the bladder wall for bacterial culture or cytology of bladder tissues;
Abdominal x-rayincluding radiopaque agents. Allows you to identify uroliths in the kidneys and bladder, areas of narrowing or expansion of the urethra, ureters, pelvis, violation of the integrity of the wall of the MP.
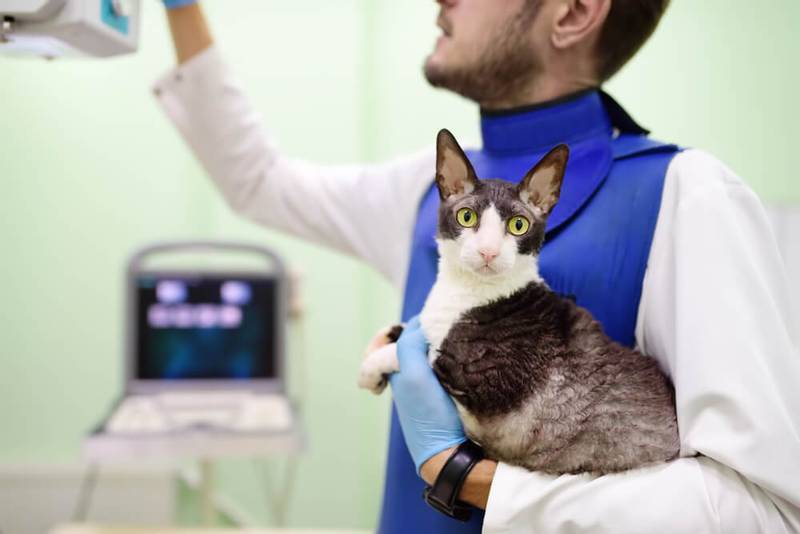

Treatment of cystitis in cats and cats
The question of how to treat cystitis in a cat cannot be answered unambiguously. There is no magic pill.
It depends on the duration of the disease, the cause of the development of cystitis, the individual characteristics of the pet, how long it takes for cystitis to pass in cats.
Inflammation of the bladder should be treated comprehensively. Drugs for the treatment of cystitis in cats are aimed at relieving symptoms
– once, to fight the cause – two, to prevent relapse – three.
Do not self-medicate, let the doctor decide which pills to give the cat for cystitis. Many human drugs are not only dosed differently, but are also deadly to animals.
For cystitis, a doctor may prescribe the following:
Antispasmodic drugs;
Painkillers (NSAIDs), provided there are no contraindications;
Antibiotics. A long course of at least 10 days, with the control of urinalysis until the antibiotic is discontinued. So you can adjust the duration of application;
Preparations containing glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). Designed to restore the inner wall of the bladder. When prescribed by a doctor, they are safe, but there is still little evidence of their effectiveness;
Diets with acidifying/alkalinizing supplements to correct urinary pH;
Increasing water consumption;
Specialized diets for a long time;
Pheromone preparations for cats to reduce stress;
Antidepressants. Strictly prescribed by a doctor, they are used in cases where the pet continues to experience stress, despite the improvement in living conditions, treatment and the use of pheromones.
We remind you: how and how to treat cystitis in a cat, the doctor will decide after examining and receiving the results of the research.
According to the form of release, the preparations are different: drops, tablets, injections, food supplements for cystitis for cats. Ask your doctor to choose the most convenient way for you to administer the medicine, because the main thing is to maintain trust and love between you and your pet.
The timeliness of treatment and the implementation of the doctor’s recommendations directly affect how long cystitis is treated. On average, treatment can take from a couple of weeks to several months. For example, the treatment of urolithiasis can take several months, and bacterial cystitis without complications is treated in a couple of weeks.
Sometimes drops are used for cystitis in cats.
Measures to prevent cystitis in cats
We discussed how to cure cystitis, but how to prevent relapses?
Prevention of cystitis in cats is very important and consists of four simple rules:
Sufficient water intake. It is important to make sure that the cat drinks about 40-50 ml / kg / day. Place bowls of water in areas where your pet likes to spend time. You can use vessels of different shapes and materials: plastic, glass and metal; glasses, bowls and plates, even buckets, the main thing is that the cat drinks more. Try adding a couple of drops of milk or broth to the water and change it regularly. You can increase your fluid intake with wet diets;
Balanced diet. We will talk about it in detail in the next section;
Physical activity. Normally, cats should move a lot. Find a way to stir up your Murzik: teasing toys, laser pointers, bows, paper balls, etc.;
Stress reduction. Is your pet afraid of guests, hiding from the noise, and visiting the clinic is accompanied by terrible screams? The following recommendations will help you:
The pet should have a separate tray in a fairly secluded place. There should be several scratching posts in the apartment. It is better to place them not where it is convenient for you, but where it is convenient for your pet: next to bowls, on window sills, on the corners of furniture or walls that he likes to rub against. Special houses and complexes can help. Cats feel more comfortable when they spend a lot of time upstairs. If there are high places in the apartment that you do not use, put a bed there, let it be a cat’s observation point. Regular games and rewards will also help. And, of course, sedatives with pheromones. They create a cat-friendly atmosphere in the home and promote a more relaxed behavior.

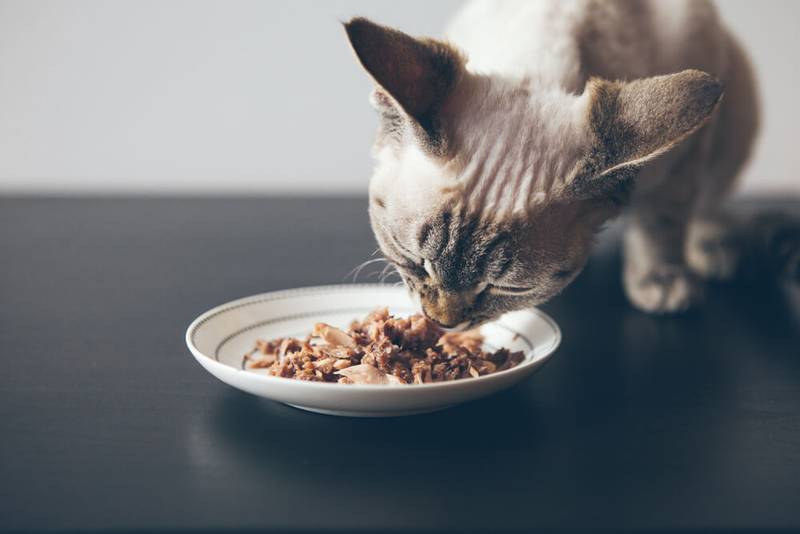
What to feed a cat with cystitis during treatment?
Regardless of the type of cystitis, it is important to provide the pet with an abundant supply of moisture to the body. When the pH level of the urine changes, the addition of acidifying/alkalinizing additives is required. And, of course, you need to take into account such a complication of cystitis as urolithiasis, so you need to monitor the level of crystal-forming substances in the diet (P, Ca, Mg, etc.) and feed accordingly.
If the cat eats industrial rations, during the period of illness it is worth giving preference to wet food. The therapeutic diets contain acidifying additives to change the pH of the urine, and they contain a minimum of crystal-forming components, as well as substances that stimulate thirst.

If you stick to homemade diets, then you need to also provide plenty of moisture. Food can be salted, but without excitement. Cats need salt, but it should not be in excess. In small quantities, it will be useful, as it stimulates thirst. It is better to exclude foods high in P, Ca, Mg: meat, fish, cottage cheese. Limit the level of protein in the diet to a physiological minimum.
Veterinary nutritionists in the Petstory mobile app will help you create the right diet. You can download it .
The article is not a call to action!
For a more detailed study of the problem, we recommend contacting a specialist.
Ask the vet
October 7 2020
Updated: February 24, 2021