Cough in dogs: what happens, causes, treatment
Contents
- Why is the dog coughing
- Types of cough in dogs
- Concomitant symptoms
- Diagnosing a cough in a dog
- Cough when a foreign body enters the respiratory tract
- Enclosure (kennel) cough in a dog
- Features of a cough in a dog with certain diseases
- Cough in small dogs
- Dog coughing fit: what to do to prevent choking
- How to treat a cough in a dog
Why is the dog coughing
Causes of cough in dogs can be very diverse. Conventionally, they can be divided into two groups: those associated with diseases of internal organs and household ones. Among the first are often found:
- bacterial, viral, fungal infections of the nasopharynx, respiratory tract, lungs;
- heart diseases;
- allergies;
- neoplasms;
- helminthiasis.
The factors of the second group that provoke the cough reflex in an animal include the following.

Check to see if the collar is too tight in your dog’s throat – it may be the cause of the cough
- Tight collar. The dog coughs when overstretched (“so as not to run away”) if the collar becomes small while pulling on the leash. The latter is especially typical for young, too active pets. Often, a cough is associated with a leash in dogs with a too short or, conversely, long neck. In the first case, it is preferable to use a harness, and in the second, carefully select the width of the accessory.
- Accumulation of hair in the esophagus and stomach. The problem is typical for quadrupeds with long hair. When licked (although not often), the dog involuntarily swallows hair that does not move along the digestive tract, but gradually gathers in a lump in the stomach or esophagus. Such accumulations lead to a gag and cough reflex. In this case, the dog coughs as if choking.
- A foreign object is stuck in the throat. Anything can get stuck: a thread, a New Year’s “rain”, a bone from a fish, a chicken. The thread, if not completely swallowed, will irritate the mucous membrane of the oropharynx and esophagus for a long time, causing coughing and vomiting. Sharp bones, piercing into the tissues of the oral cavity, pharynx, esophageal wall, not only create a sensation of interference in the animal, but also lead to inflammatory processes (suppuration, pain, swelling of the mucosa, and others).
- Features of the anatomical structure of the respiratory tract, oropharynx and esophagus of the pet. For short-faced animals, the so-called reverse sneeze is characteristic. This is a paroxysmal cough, not associated with diseases, which occurs abruptly and passes quickly, without outside help.
Types of cough in dogs
Cough in dogs is classified based on several characteristics. It is important that the owner, contacting the veterinary clinic, could tell in sufficient detail about each of them.
Presence/absence of sputum
- Wet (with mucus)
- Dry (without it)
The nature of the flow
- Acute (appears sharply, pronounced)
- Subacute (develops progressively, gradually intensifying)
- Chronic (lasts long)
Severity of manifestation
In addition, there is a seasonal cough – an allergic reaction of the pet’s body to changes in nature.
Concomitant symptoms
Coughing in dogs can occur on its own or be accompanied by other symptoms. Among them:
- vomiting;
- an admixture of blood in the sputum;
- frothy discharge from the mouth;
- temperature increase;
- refusal of food;
- weakness in the muscles (the animal moves with difficulty);
- respiratory failure, shortness of breath and so on.
Some diseases develop rapidly, can lead to the death of a pet. In case of a sudden deterioration in the condition of the dog, you should immediately consult a veterinarian.
Diagnosing a cough in a dog
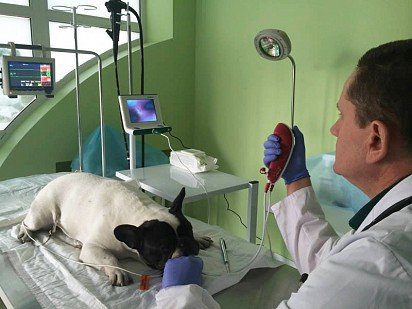
A cough in a dog can cause serious illness, so it is recommended that you take your pet to the veterinarian for a checkup.
At the appointment with the veterinarian, the pet will be examined, and the owner will be questioned. It will be necessary to talk about the features of cough, its prescription, the conditions accompanying the occurrence. You will need to provide information about the age of the dog, the presence of any diseases, vaccinations, conditions of detention, and so on. The complex of diagnostic procedures may include methods such as:
- X-ray
- bronchoscopy;
- ECG;
- cytological, bacteriological examination of sputum.
Cough when a foreign body enters the respiratory tract
As a rule, if the dog choked or swallowed something superfluous, it copes with the situation on its own by expectoration. At such a moment, the cough begins suddenly, abruptly, accompanied by appropriate movements of the neck and head, a characteristic posture.
There may be another situation: the animal choked on a sharp bone, an object that, due to its shape or size, caught on the mucous membrane. Then the following symptoms may appear:
- coughing fits, prolonged, debilitating;
- during the cough reflex, the pet tries to push the foreign body out of the throat, as it were;
- wheezing;
- difficulty breathing;
- foam from the nostrils;
- cough with blood, foam;
- refusal to drink and eat.
It is impossible to hope that the dog will cope on its own. Trying to pull out (or even see) what got into her throat is almost impossible without special tools. The animal must be urgently taken to the clinic. Delay threatens the development of emphysema, inflammatory processes in the bronchi, lungs, pleura and other complications.
Enclosure (kennel) cough in a dog
Enclosure cough is a symptom of some infectious (mainly viral) diseases of the dog, so named because of the most common cause of infection – living together or frequent contact of animals with each other. The source of infection is a sick or recovered dog.
Symptoms of the disease are due to the characteristics of the pathogen (parainfluenza, canine herpes, bordetella), as well as the state of the animal’s immune system. After the incubation period (up to 10 days) has passed, the following manifestations of the pathology are possible:
- slight paroxysmal cough, similar to the fact that the dog choked, but less pronounced;
- cough with white foam;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- increase in temperature indicators;
- lacrimation;
- discharge from the nostrils.
Kennel cough lasts about 2 weeks. The stronger the immunity of the dog, the easier it is to tolerate the infection, sometimes without even requiring special treatment. In severe cases, the use of antibacterial agents, antiviral, expectorant, immunomodulating and others is indicated (according to the results of the examination).
Features of a cough in a dog with certain diseases
The cough reflex only indicates the presence of a pathological process in the body, and is not an independent disease. What happens to a cough in dogs depends on the underlying disease. Knowing the features of the cough syndrome and the accompanying symptoms will speed up the diagnosis, and will allow the pet to receive timely treatment and first aid.
Allergic reaction
Allergies in dogs show up with a variety of symptoms. Cough may be accompanied by:

Can a dog’s cough be caused by an allergic reaction?
- discharge from the nostrils, eyes;
- swelling of the mucous membranes;
- redness of the eyes;
- sneezing
- skin rashes;
- itching and other symptoms.
The owner should observe the pet, perhaps coughing and other signs appear after eating certain foods, after a walk, are seasonal. If an allergen is detected, it is excluded from the life of the dog, and appropriate therapy is carried out.
Bronchitis
The inflammatory process in the bronchi – bronchitis – at the initial stage is accompanied by a dry, heavy cough of a pet. It is most pronounced in the morning: wheezing and whistling are heard. After a few days, the cough becomes wet, whitish or yellowish sputum appears. Among the additional symptoms of the disease should be noted shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, fever.
The owner should be aware that bronchitis can be both viral and bacterial in nature, so the treatment in both cases will be different. You can determine the pathogen “by eye” by the severity of the symptoms: in the bacterial form, they are stronger, and the dog’s condition is much worse. In addition, if bronchitis is caused by bacteria, the pet’s body temperature will be higher than normal by 2 or more degrees (with a viral infection, it rises within one degree).
Helminthiasis
The life cycle of some parasites is associated with the migration of ingested larvae from the stomach and intestines to the lung tissue. In the respiratory organs, helminths spend about 2 weeks, and then they are expectorated, swallowed along with sputum, and grow into adults already in the intestines.
Being in the lungs of a dog, worms lead to the following symptoms:
- wet cough with an admixture of blood;
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath;
- an increase in temperature, sometimes quite strong, up to 43 ˚С.
With greater certainty, it is possible to say that the cough has a parasitic cause if, shortly before these manifestations, the animal had problems with digestion, pain in the intestines, and diarrhea.
Lung infarction
Dogs with pathologies of the cardiovascular nature are at risk of developing pulmonary infarction. This may occur due to the detachment of a blood clot. A characteristic sign is a strong sharp pain, in which the animal jumps, may scream. Shortness of breath and cough with bloody mucus begin almost immediately. The dog weakens before our eyes, the mucous membranes turn pale, the heart beat is disturbed, blood pressure drops, and the temperature rises. The pet should be taken to the clinic immediately.
Laryngitis
Inflammation of the pharynx in a dog is also accompanied by a cough. At an early stage of the disease, it causes torment to the animal: a dry and persistent cough causes pain, so the pet may refuse to eat, stop barking (or making hoarse, hoarse sounds). Gradually, the cough reflex becomes productive, a small amount of sputum is released, as the inflammatory process subsides in the mucosa, pain disappears. Body temperature remains within normal limits or rises slightly.
adenovirus
This disease is of viral origin. The mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, throat is affected. Symptoms of adenovirus:
- sore throat (the animal reacts appropriately when trying to palpate);
- swollen lymph nodes under the jaw;
- productive cough;
- coughing discharge may be clear or cloudy;
- lacrimation;
- discharge from the nostrils;
- a slight increase in temperature indicators;
- refusal of food;
- in the intestinal form, vomiting, nausea, indigestion, diarrhea and pain in the intestinal region are observed.
Heart Disease
If the dog has heart defects or disease, a heart cough may develop. It is characterized by a pink color of sputum, due to the seepage of blood into the lungs through the capillary walls. Foamy pink discharge from the respiratory system is accompanied by other symptoms of heart failure:
- increased cough after physical activity;
- animal weakness;
- labored breathing;
- mucous membranes acquire a bluish tint.
Cardiac cough in four-legged friends unfortunately carries a poor prognosis. In the best case, the dog will be able to live 2-4 years. Pathology is treated only by surgery, but, due to the complexity and high cost of operations, they are not performed.
Bronchial asthma
The development of bronchial asthma in a dog can be triggered by prolonged exposure to various allergens, chemical volatile compounds, nervous stress, weather conditions, and infectious diseases. The dog coughs as if choking, accompanying the attacks with appropriate movements of the head and torso. The characteristic signs of the disease are:
- the appearance of seizures after physical exertion, their absence during rest;
- secretion of thick transparent mucus from the bronchi;
- bluish mucous membranes;
- suffocation during an attack;
- redness of the eyes;
- sneezing.
Cough in small dogs
Chihuahua coughing
Cough in dogs of small breeds is a frequent occurrence due to the peculiarities of the structure of the pharynx, respiratory tract, maxillofacial apparatus, and the location of the teeth. So, due to the accumulation of bacteria, insufficient hygiene of the oral cavity and teeth, the pet may develop gingivitis, stomatitis and other inflammatory processes. The infection gradually passes to the mucous membrane of the larynx, trachea, settles in the pharyngeal tonsils, descends into the lungs.
The deep location of the tonsils plays an important role in the development of inflammation and cough. Their increase in response to an infectious invasion leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the larynx, shortness of breath, shortness of breath. If this situation is repeated often, then the tonsils must be removed. As a preventive measure, the owner of a small dog should regularly show the pet to the veterinarian in order to timely identify and eliminate problems with the teeth and oral cavity.
Dog coughing fit: what to do to prevent choking
It’s one thing for a dog to choke or cough, but it handles the situation on its own. However, it happens that the pet needs outside help – the attack can be prolonged, and the animal begins to choke. You can prevent suffocation by applying a few recommendations.
- If this is an attack of reverse sneezing, then swallowing the saliva accumulated in the oral cavity and taking a deep breath should be ensured. This is achieved by pinching a four-legged friend’s nose or running his hand over his throat several times.
- It is advisable to turn the pet over so that the head is lower than the body and limbs. You can shake the animal, make a series of claps on the back. With a large pet, you can raise the hind legs (the dog must stand) and also make a few claps at chest level.
- In short-faced pets, the airways may be blocked by the surrounding soft tissues. If the dog is choking, you can check the free passage of air with your finger.
- If the animal is not breathing, it is urgent to start resuscitation: ensure the supply of oxygen to the respiratory system and massage the heart area.
Attention: after such an attack, the animal must be shown to a veterinarian.
How to treat a cough in a dog
Before treating a cough in a dog, you need to find out its cause, because sometimes even hospitalization of the animal may be required. Or another option is coughing as a symptom of a cold. Such a phenomenon in most cases goes away on its own within two to three days, and any attempts by the owner to “cure” it with antitussives can only do harm. However, if the symptom does not go away, intensifies, others join it, then you must definitely contact a specialist and do an examination.
When coughing in dogs, treatment at home or in a hospital is possible, but in any case it will be complex. Depending on the cause of the pathology, therapy involves taking such groups of drugs as:
- antibiotics (penicillin, chloramphenicol);
- antiviral (fosprenil);
- anti-inflammatory (dexamethasone);
- immunomodulating and immunostimulating (interferon, ribotan);
- cardiac (cordiamin);
- antidiarrheal (loperamide);
- antipyretics (paracetamol, ibuprofen);
- antihistamines (allerveta, diphenhydramine);
- antihelminthic (polytrem, arecoline);
- expectorants (broncholithin);
- antitussives (mukaltin, bromhexine).
In addition, the composition of complex therapy can include anti-vomiting drugs that improve digestion, painkillers, restorative and many others.
Attention: due to the numerous options for the origin and further development of a cough in a dog, it is highly recommended not to treat the animal without a preliminary examination and consultation with a specialist.
Treating a cough in a dog is not limited to medication. The owner is required to create the most comfortable conditions: providing good nutrition (if necessary, taking vitamins), the absence of drafts. If it is cold outside, the walking time should be reduced to a minimum.
You can alleviate the condition of the dog by arranging a kind of “inhalation”. To do this, in urban conditions, the bathtub is filled with hot water so that the air becomes humid. The pet must be brought into the bathroom so that it breathes steam for 10-15 minutes. Such a procedure will not only facilitate the discharge of sputum, but also eliminate the swelling of the mucous membranes, reduce pain, and normalize breathing. In water, you can add decoctions of fir, eucalyptus, chamomile and other plants, sea salt.
Since coughing in dogs is just a symptom that indicates the presence of the disease, it is important to contact the clinic in time. Thus, the owner will prevent the development of complications in the pet, preserve his health, and also avoid additional material costs in the future.