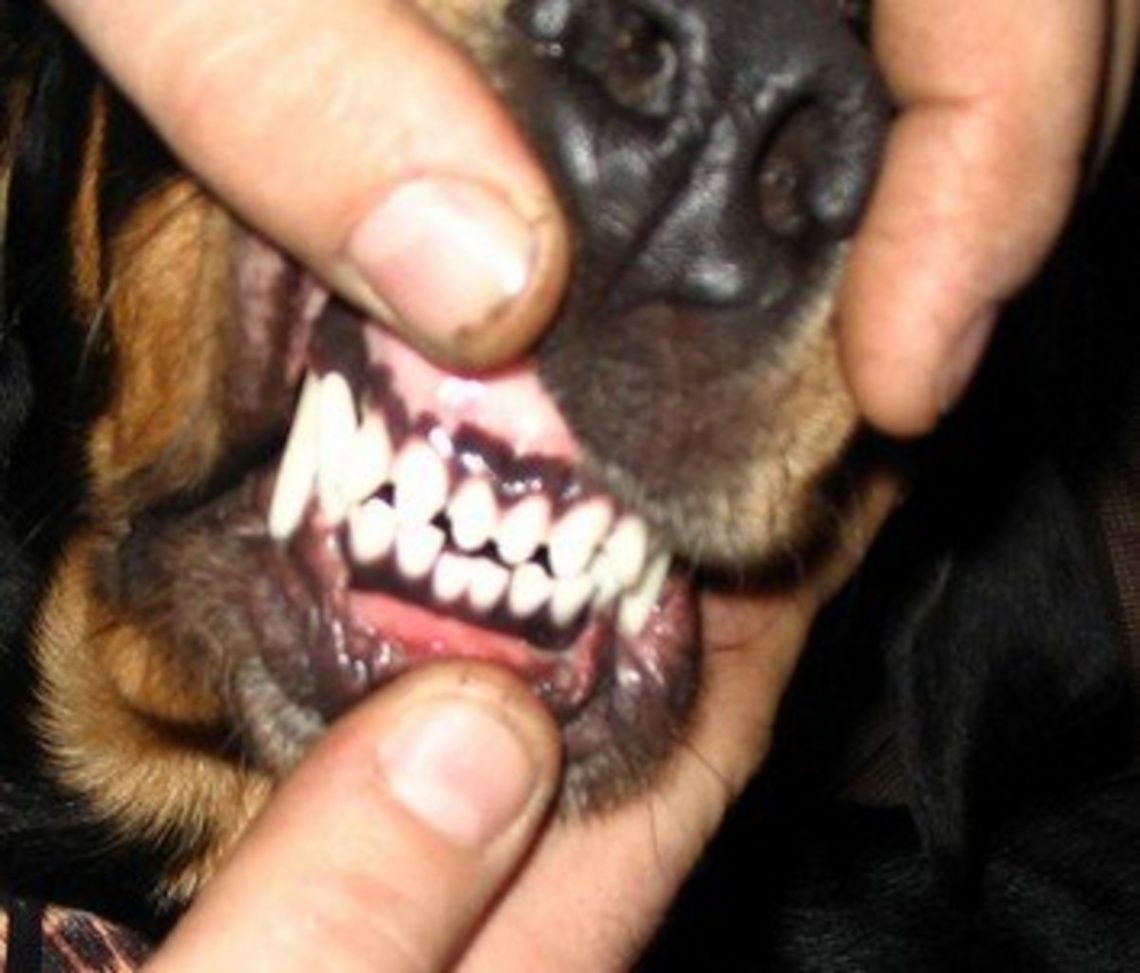
Correct and incorrect bite in dogs

Contents
Features of bite in different breeds
Each breed has its own head and jaw shape, and what would be considered normal for an English Bulldog, for example, would be completely abnormal for a Husky. Consider the types of bite in dogs belonging to different breeds.
A dog has 42 teeth – 12 incisors, 4 canines, 16 premolars and 10 molars. Each group of teeth has its own function and position. The incisors are located in front and are necessary for biting, biting, it is with them that the dog gnaws out parasites from wool and foreign objects. Fangs help to capture food, are necessary for hunting and look threatening. Premolars are located immediately behind the fangs, 4 pieces at the top and bottom, right and left, they crush and tear pieces of food. The molars, the furthest teeth, 2 on the upper jaw and 3 on the lower jaw on each side, their task is to grind and grind food.
The correct type of bite is observed in dogs with a narrow muzzle, such as spitz, toy terrier, collie, greyhounds. It is called a scissor bite – 6 incisors, upper and lower, in the dog lie flat on top of each other, and 4 canines are exactly located between each other, without sticking out or sinking into the mouth.

While pets with a brachycephalic type of muzzle have a square head and short jaws. These breeds include pugs and chihuahuas. The shortened jaw contributes to the fact that in such dogs the absence of 1-2 teeth is not considered a pathology, since the entire set simply cannot fit. The closure of the jaw should also be even, tooth to tooth.
It is normal for a Bulldog, Pekingese and Shih Tzu in conformation to have the lower jaw protrude strongly forward. From the point of view of physiology, this, of course, is not the norm, and later in the article we will analyze what this can lead to.
Correct bite in dogs
In normal occlusion, the upper jaw overlaps the lower dentition.
The canines of the lower jaw are equidistant between the upper canines and the third lower incisor, and the premolars indicate the spaces between the teeth of the upper jaw. The classic correct bite in a dog is considered a scissor bite. This is the most suitable option for dogs, as they are hunters. Their task is to hunt, grab and hold prey. The incisors fit snugly together, the fangs are “in the castle”. Due to this position, the teeth wear out less, and as a result, they do not collapse and do not fall out. A scissor bite is normal for any long-nosed dog. For example, for Dobermans, Jack Russells, Jagd Terriers, Yorkshire Terriers and others.
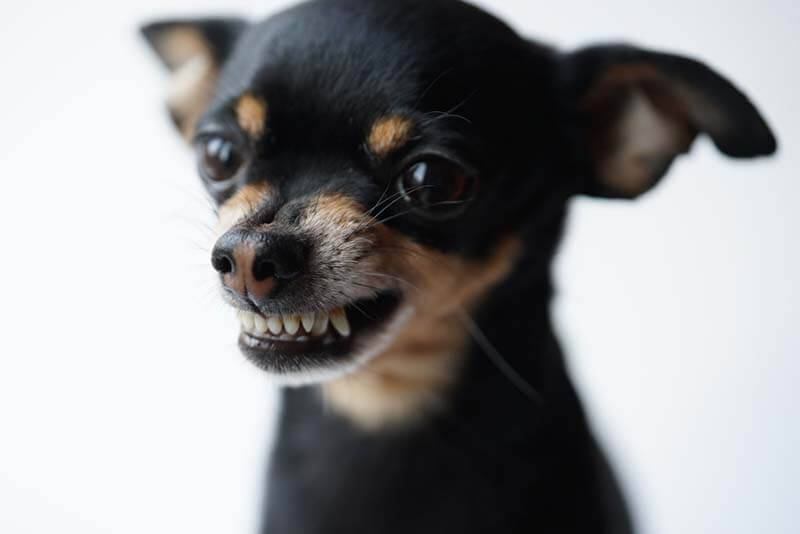

Malocclusion in dogs
It occurs when variations from the classic scissor bite are present, which may be caused by misalignment of the jaws or dentition. Malocclusion in dogs is called malocclusion. It is considered that this is any deviation in the closing of the teeth. Incorrect closure of the jaw changes the exterior of the head, the tongue may fall out, the dog has difficulty grasping food.
Pincer bite or pincer bite
With this type of bite, the upper jaw, closing, rests with incisors on the lower incisors. They create one line, the rest of the teeth do not close. In such dogs, the incisors quickly wear down and fall out, the pet cannot grind food normally, since the molars and premolars do not touch. This type of bite is not considered a conditional norm in brachycephalic breeds and does not affect the assessment of the exterior.
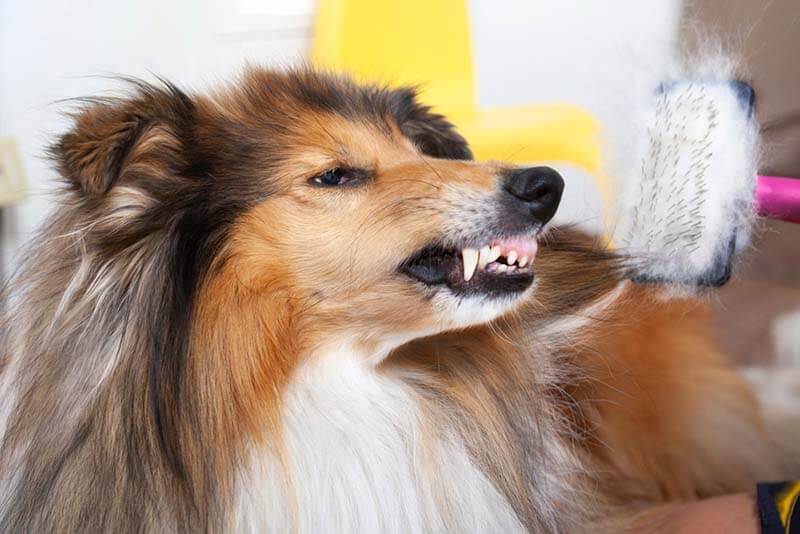

Undershot or prognathism
Undershot bite is a serious deviation in the development of the bones of the dog’s skull. The lower jaw is underdeveloped, it is short. As a result, the lower teeth come into contact with the upper palate and gums, injuring them. The tongue protrudes from the mouth. Due to underbite, diseases of the dentition develop – erasure of fangs and molars, tartar, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, since it cannot normally capture and grind food.
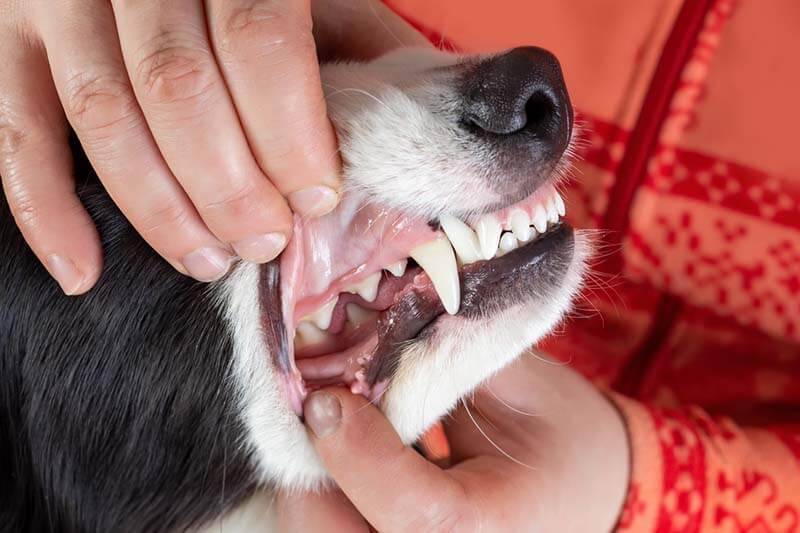
Snack or progeny
This malocclusion is characterized by a shorter upper jaw and a longer lower jaw, resulting in the lower teeth in front of the upper teeth. While this condition is normal for some breeds, it is unusual for most pets. Overbite in dogs with a long muzzle is considered a pathology, while in griffins, Pekingese, bulldogs and other short-muzzled breeds, it is allowed. The lower jaw protrudes forward and gives the face a rather businesslike and disgruntled look. Often when the lower jaw protrudes, the teeth are completely exposed and not covered by the lips – this is called undershot bite. If the distance between the teeth of the lower and upper jaws of the dog is insignificant – a snack without waste.
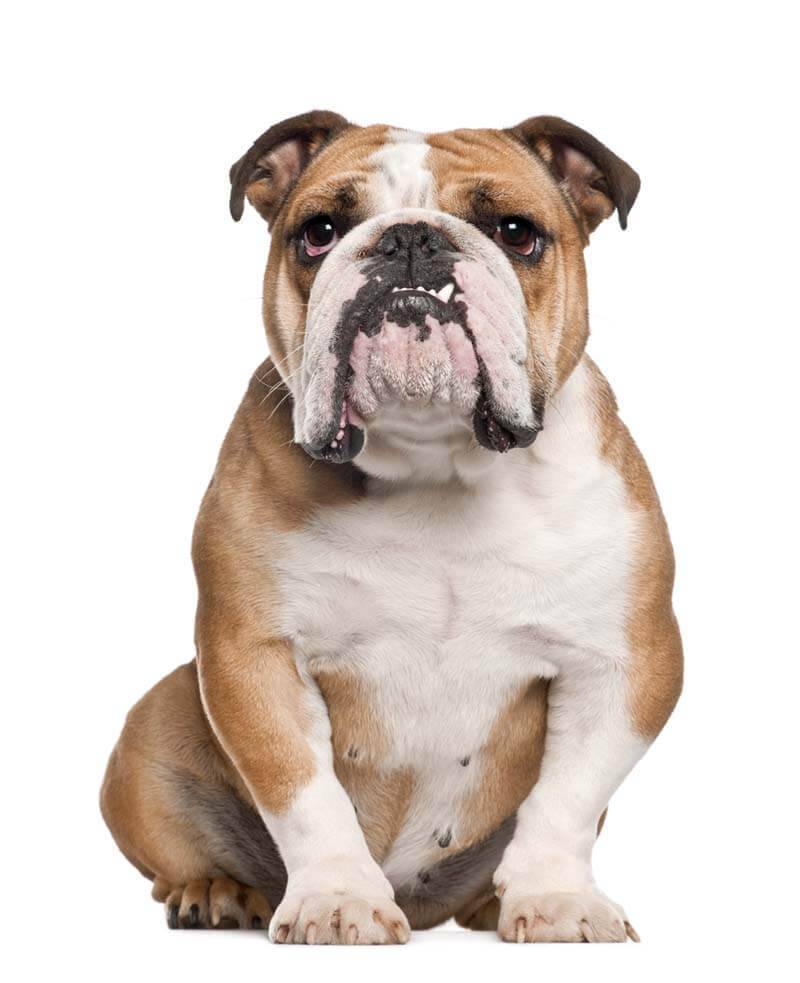

Open bite
The anterior teeth do not meet and leave a gap, often the dogs will push their tongue into it, which increases the separation, especially in young individuals. In Dobermans and Collies, it is often manifested by non-closure of premolars and molars, and not incisors.
Jaw distortion
The most difficult and dangerous deviation in the development of the jaw, as the bones grow unevenly or change their size as a result of injury. The jaw of the dog becomes asymmetrical and distorted, the incisors do not close.
Improper growth of teeth
Most often, deviations in the direction of growth have fangs. They can grow in or out of the mouth, causing the jaw to not close or trauma to the palate. Often in dogs of brachycephalic breeds, the growth of incisors in a checkerboard pattern is found, for them this is considered a conditional norm.
Polyidentity
Polydentia can be false or true. With false polydentia, milk teeth do not fall out, and molars are already growing. This affects the direction of tooth growth and, as a result, the closing of the jaw. With true polydentia, two develop from the rudiment of one tooth, as a result, the dog may have two rows of molars, like a shark. This is not normal and affects the condition of the jaw, tartar formation, bite formation and food grinding.
The reasons for the wrong bite
Causes of malocclusion can be congenital, genetic, and acquired throughout life.
Congenital malocclusion cannot be prevented, and normal malocclusion in parents is no guarantee that their offspring will not have deviations in jaw closure and tooth growth.
Genetic abnormalities in the development of the jaw most often cannot be corrected.
These include undershot and undershot. This is usually found in pedigreed pets with selective breeding.
In puppies, this can be temporary when one jaw grows faster than the other, and there is a gap that goes away as they get older. Also, in young dogs, there may be a slight discrepancy before the change of milk teeth to molars, since the size of the milk teeth is smaller than the permanent ones.
Often you can find the opinion that the bite is spoiled by wrong games, bones. This can rather be attributed to myths, since we have already indicated that the size of the jaw is a genetically determined deviation.

With acquired deviations, everything is more difficult, and they are affected by the conditions of detention, feeding from the moment the organism is formed. Acquired bite defects can lead to:
Incorrect replacement of teeth or non-loss of milk teeth. More common in small dog breeds – Spitz, Toy Terrier, Chihuahua, Yorkshire Terrier;
Lack of vitamin D and calcium in the diet at an early age and during the period of fetal maturation during pregnancy in bitches. Common in dogs on unbalanced natural diets;
Jaw injuries of any etiology (cause), hard toys in small puppies, or the consequences of blows.
Most often, acquired deviations are formed in a dog at an early age or in the womb, it is also possible to correct this condition in the early stages.
Danger of malocclusion
Incorrect bite in a dog, in addition to the aesthetic side and violation of the exterior, can lead to health problems.
Tartar, periodontitis, early abrasion and loss of teeth, stomatitis, trauma to the gums, lips and palate – all these are the consequences of improper tooth growth or underdevelopment of the jaw.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract may also occur. With an incorrect bite, the animal cannot grind food, grab it and keep it in the mouth, which leads to quick eating or, conversely, a poor diet, as a result, diseases of the stomach develop – gastritis, pancreas – pancreatitis and intestines – enterocolitis.
Overexertion of the neck muscles also appears in animals with malocclusion. More often this happens with large pets who pull ropes in games, wear sticks. A dog cannot properly grasp and hold an object in its mouth if the jaw is not fully closed, causing it to use and tense the neck muscles to complete the task. In such animals, the neck is bent, tense, the muscles are in hypertonicity, they hurt.
Correction of malocclusion in dogs
Correction of bite in dogs is a complex and not always possible procedure. It takes several months and sometimes does not lead to an ideal bite, but only allows you to get closer to it.
To change the length of the jaw, surgical methods of treatment are used, unfortunately, they are not always effective and the possibility of their use depends on the difference in the lengths of the jaws.
To change the setting of teeth and the direction of their growth to normal, orthodontic appliances of a removable and non-removable type are used:
Bracket system. Braces locks are glued to the teeth, an orthodontic arch with springs is installed on them, they attract or push the teeth, changing the direction of their growth.
Orthodontic plates. An impression of the dog’s jaw is made, then a plate is cast over it and placed in the oral cavity. It is important that it fits exactly in size and does not injure the gums and oral mucosa.
Gingival rubber tires. Locks are attached to two teeth and a special elastic orthodontic chain is pulled between them, it pulls the teeth together. Tension is controlled by shortening the links in the chain.
Kappa. Acrylic caps for teeth. They are put on top of the entire dental apparatus and correct the position of the teeth with pressure.
The method of correction is chosen individually for each pet by an orthodontist, as it depends on the degree of divergence of the teeth, the direction of their growth and the cause of the malocclusion.
Prevention
The dog’s bite, first of all, is affected by a properly composed diet. It is important to take into account the needs of the dog in vitamins and trace elements, taking into account its age and size. When feeding with natural food, it is necessary to use complexes of vitamin and mineral supplements, a nutritionist will help control this. On dry diets, it is enough to feed with a food line that is suitable for the age and weight of the dog, since the manufacturer has already taken everything into account. It is also important that mothers get enough vitamin D when they are pregnant, as this will affect the development of bones and teeth in the fetus.
The oral cavity should be examined regularly.
All teeth should be straight, in the same line, of the same color. Gums – light pink or pink, without swelling. The smell from the mouth cannot be pungent and strong.
Choose the right toys. Their rigidity and size depends on the size of the dog’s jaw and its strength. The type of game is also important. For example, it is difficult to assess your strength when playing tug-of-war, it can damage your teeth.
Exclude tubular bones, logs, and plastic from your pet’s access.

Bite in dogs is the main thing
A correct bite is called a scissor bite, and any deviation from it is referred to as a malocclusion.
For the formation of the correct bite, it is important to maintain a balance of vitamin D and calcium in pregnant bitches and offspring.
Different breeds may differ in the conditional norms of the correct bite. The shape of the head affects the position of the teeth, their number and the length of the jaw.
Occlusion pathologies lead to the development of chronic injuries of soft and hard tissues of the teeth, the animal is unable to properly close the jaws and eat.
To treat malocclusion, orthodontic appliances are installed, the choice of treatment method depends on the cause and type of malocclusion.
Malocclusion, caused by a genetic factor, cannot be treated.
Answers to frequently asked questions