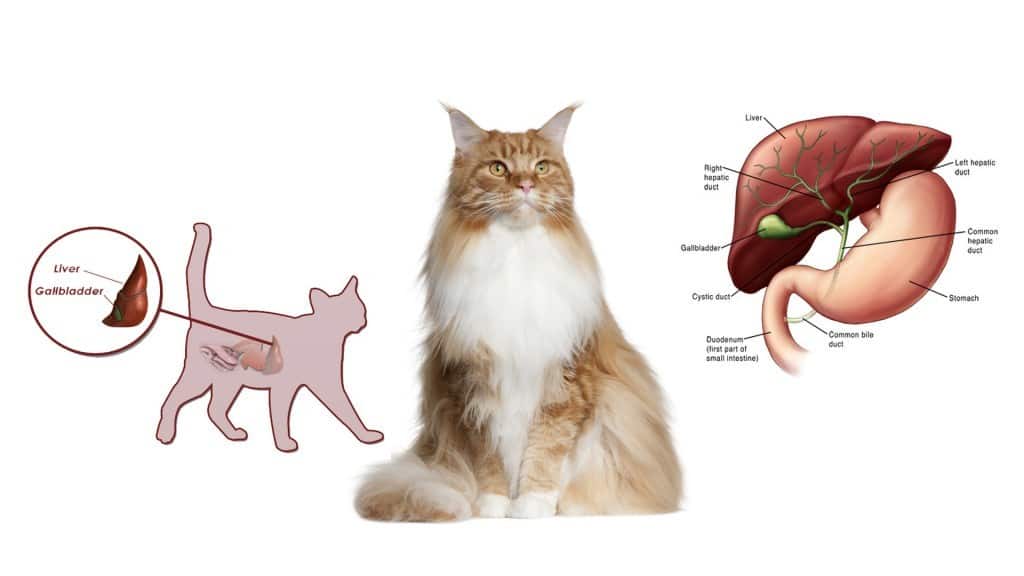
Cirrhosis of the liver in cats and cats

Contents
Liver Cirrhosis in Cats: Essentials
Cirrhosis of the liver is a chronic disease in cats, predominantly occurring in the elderly.
The causes of the disease are diverse, sometimes it is extremely difficult to establish the exact cause.
The main symptoms include vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, refusal to eat.
There is no cure for cirrhosis in cats, but it is possible to slow down the process and improve your pet’s quality of life.
Types of disease
In a healthy animal, the liver consists of large lobes, which in turn consist of smaller lobes. In areas of cell death due to cirrhosis, so-called “regeneration nodes” appear, which replace normal lobules. According to the morphological characteristics, cirrhosis of the liver in cats can be divided into the following types:
Small-nodular (micronodular)
With this type of liver cirrhosis in cats, the regeneration nodes have a small diameter, most often they capture only one lobule of the liver.
Large-nodular (macronodular)
Regeneration nodes are larger, may affect several adjacent lobules or be located in different lobes of the liver.
Mixed (small and large-knot)
Has signs of both types of cirrhosis.
Depending on the location of cirrhotic changes, it is customary to distinguish:
Portal cirrhosis (in the region of the portal vein of the liver);
Cardiac cirrhosis (in the region of the central vein of the liver);
Biliary cirrhosis (in the area of the bile ducts).
You can also distinguish types of liver cirrhosis in cats for the reason that caused it:
Primary (toxic substances, drugs);
Secondary (viruses, bacteria, parasites, diseases of the bile ducts, heart disease, chronic hepatitis and hepatosis).
Causes of the disease
The causes of liver cirrhosis in cats and cats are varied. They can be divided into several groups:
Toxins
It is not uncommon for cats to eat any poisonous substances. These include eating indoor flowers (palms, lilies, spurge, dracaena). Chewing gums and toothpastes for humans contain xylitol, which is poisonous in animals. Ethylene glycol, found in antifreeze, is also often attracted to animals because of its sweet taste. Batteries in the cat’s stomach begin to oxidize and release heavy metals. Pine oil can be found in household detergents, and if eaten regularly in small amounts, it can cause cirrhosis of the liver in cats.
Medications
Some drugs have high hepatotoxicity in cats. First of all, paracetamol should be attributed to them. Unlike humans, the cat’s liver is not able to neutralize the toxic effects of paracetamol, which causes severe poisoning, sometimes death occurs even faster than changes in the liver appear.
Another hepatotoxic drug for cats is ketoconazole, its damaging effect on the liver is not as pronounced as when taking paracetamol, but with prolonged use it can also cause toxic effects.
Organophosphates and pyrethroids are found in many antiparasitic drugs, but often cause poisoning in cats. Other potentially dangerous drugs – anticonvulsants, antibiotics, glucocorticoids – with long-term use also lead to cirrhosis of the liver in cats.
Infections and infestations
The main infections that cause liver damage, including cirrhosis in cats, are leukemia virus and feline infectious peritonitis virus. The bacterial infection leptospirosis is somewhat less common, it is more common in dogs. Helminthiasis of the liver (opisthorchiasis) occurs mainly in the northern regions, infection occurs when eating raw fish.
Heart diseases
The development of liver cirrhosis in cats is possible even due to the presence of heart disease. Heart failure leads to an increase in central venous pressure, which is transmitted to the liver through the inferior vena cava and hepatic veins. There is stagnation in the circulatory system, which is why liver cells die.
Diseases of the biliary tract
Chronic inflammation and obstruction of the bile ducts can also lead to liver cirrhosis in cats.

Symptoms of cirrhosis of the liver
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis in cats are varied and depend on the stage of the disease. You may notice rapid fatigue. The cat sleeps more, with physical exertion it quickly gets tired. Decreased body weight. Appetite may be reduced, and thirst, on the contrary, increased. There is vomiting, including bile. Diarrhea can be replaced by constipation. Urine may be brown in color, and feces, on the contrary, lighter. Mucous membranes and even the entire skin may acquire a yellow tint. Often there is an increase in the volume of the abdomen due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. The process of blood coagulation is disturbed, subcutaneous hemorrhages and bleeding may occur. In the last stages of liver cirrhosis, cats develop hepatic encephalopathy, which is accompanied by convulsions, impaired coordination, and various degrees of impaired clarity of consciousness. The disease can result in the death of the pet.
Diagnostics
A large number of different studies are required to make a diagnosis. You need to find out if there could be poisoning with some toxins or drugs, if the cat eats home flowers, if raw fish is present in the diet.
It is necessary to conduct a thorough examination and palpation. Conduct various laboratory tests, including general clinical and biochemical blood tests. With cirrhosis of the liver in cats, blood tests can reveal anemia, an increase in the level of bilirubin, liver transaminases. In the last stages of the disease, liver enzymes in the blood may be within the normal range, this is due to the complete death of liver cells. A decrease in blood protein levels may be noted, and there will often be fluid in the chest or abdomen. Sometimes there are reduced levels of glucose and urea. An increase in the level of bile acids in the blood can be noted, which will indicate the formation of secondary hepatic shunts. A blood test for leukemia virus and feline infectious peritonitis virus is necessary, and a blood test for leptospirosis may be indicated.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is mandatory, special attention is paid to the liver, bile ducts, and lymph nodes. If heart disease is suspected, an ultrasound of the heart and an ECG are also performed.
In the presence of ascites or hydrothorax, the fluid is diagnosed, its cytological composition, biochemical examination, and, if necessary, seeding.
Sometimes a definitive diagnosis can only be made after a liver biopsy. Often, a biopsy can be performed by inserting a long needle into the liver under ultrasound guidance, in some cases, a diagnostic operation is indispensable.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis in cats
Unfortunately, liver disease in the stage of cirrhosis in cats is incurable, that is, dead cells are not able to recover and permanently lose their functions. Treatment is to slow the progression of the disease and maintain a good quality of life for the pet. The use of special therapeutic industrial diets is indicated, a natural diet should be developed by a veterinary nutritionist.
In case of dehydration, water-salt solutions are prescribed in the form of intravenous or subcutaneous droppers. Various vitamins are used, mainly vitamin B12 and E. In case of a violation in the blood coagulation system, vitamin K is used. Preparations from the group of hepatoprotectors can be used, their beneficial properties are still controversial, but S-adenosylmethionine and fruit extract are among the most effective milk thistle.
If a bacterial infection is confirmed, antibiotics are used, but sometimes they are justified even without a confirmed infection.

Prevention of cirrhosis
To prevent the development of cirrhosis of the liver in cats and cats, it is recommended to follow some rules. Annual vaccination can protect your pet from various infectious diseases, including such a dangerous infection as the feline leukemia virus.
The diet should include only high-quality industrial feed. If you want to feed your pet with a natural homemade diet, you need to draw up an individual nutrition plan with a nutritionist. You can even do this online – in the Petstory mobile application, you can sign up for a consultation with a veterinary nutritionist, the cost of such a consultation is 599 rubles. You can download the application from the link.
Regular treatment of the animal from helminths is shown, for a domestic cat it is at least 2 times a year. If the cat has access to the street or eats raw meat, the frequency of treatments increases to 1 time in 1-3 months.
It is possible to use various medications – for example, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant, only as prescribed by a doctor.
If a cat occasionally eats houseplants, it is best to remove them completely from her access.
At the annual medical examination, liver disease can be detected at an early stage. If you start timely treatment, you can avoid the development of cirrhosis in cats with a high degree of probability.
The article is not a call to action!
For a more detailed study of the problem, we recommend contacting a specialist.
Ask the vet
April 12 2021
Updated: 21 May 2022