Blue tongue in dogs

Contents
- About cyanosis
- Why does a dog have a blue tongue – 10 reasons
- Norm for some breeds
- Narrowing of the lumen of the trachea or collapse of the trachea
- Violation of the integrity of the respiratory tract
- Insufficiency of respiratory muscles
- Accumulation of air or fluid in the chest
- Pulmonary edema of any origin
- Heart pathology
- Elongation of the veil of the palate – brachycephalic syndrome
- Bronchitis
- Eating pigmented foods
- Concomitant symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
- Blue tongue in dogs: summary
- Answers to frequently asked questions
About cyanosis
Oxygenated blood is bright red, so the tongue should normally be pale pink to pink.
Altered, not oxygenated blood of a blue, brown hue, therefore, a blue, purple tongue and the inner surface of the cheeks, gums indicate an acute manifestation of oxygen deficiency of any origin in a pet.
Types of cyanosis
With false cyanosis cyanosis is observed due to the ingress of dyes into the blood or on the surface of the tongue, which are deposited in the skin and mucous membranes.
True cyanosis – a manifestation of heart or respiratory failure, characterized by the accumulation in the blood of a large amount of hemoglobin that is not saturated with oxygen.
With central cyanosis cyanosis occurs as a result of violations of the central circulatory system. Its occurrence is due to a significant decrease in the level of oxygen in the blood of the body – cyanosis appears on the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth, conjunctiva of the eye (mucosa), etc.
peripheral cyanosis – a disorder characteristic of one organ or one part of the body. This may be an injured limb or an organ with a violation of the circulatory system.
Why does a dog have a blue tongue – 10 reasons
Norm for some breeds
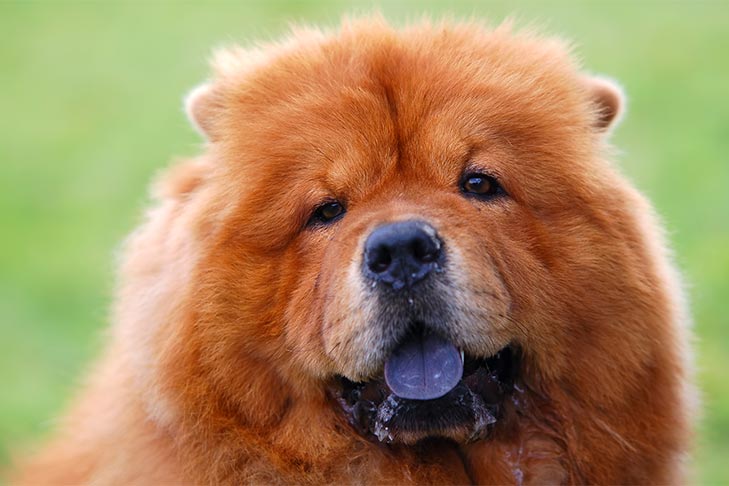
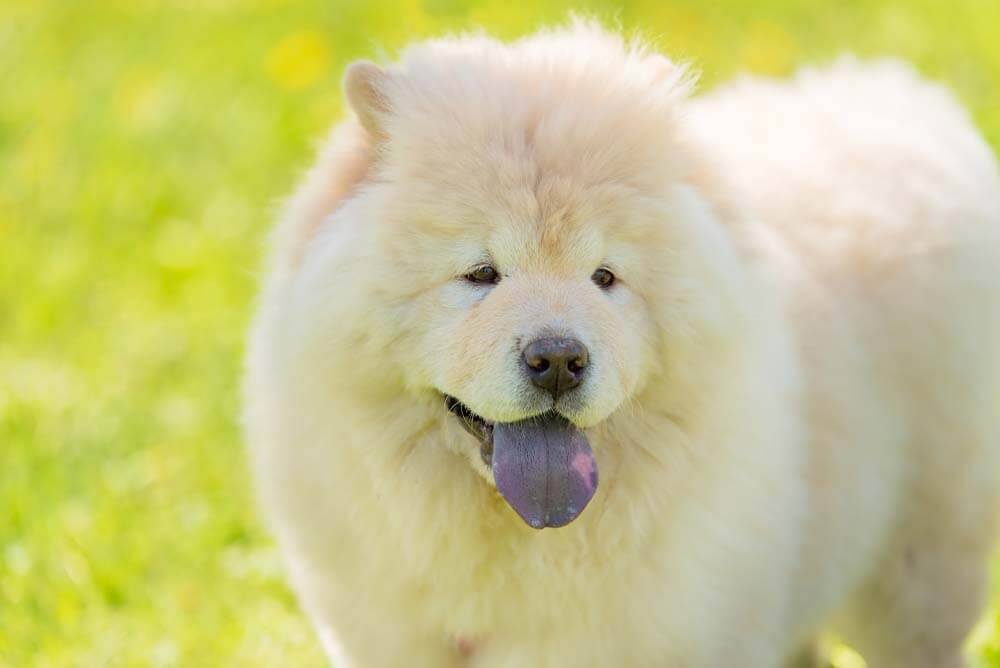
Pigmented mucous membranes can be normal in almost any breed, but are most commonly seen in Chow Chows and Shar Pei. In this case, this coloration is observed in the dog throughout its life.
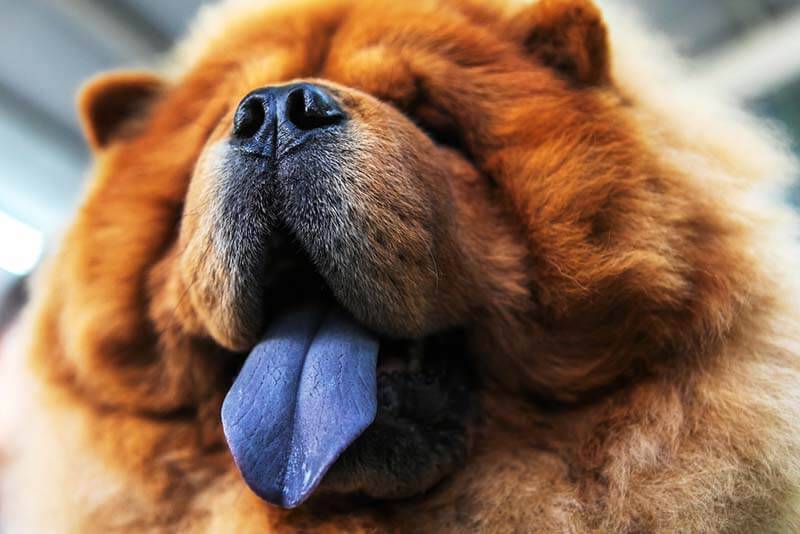

Narrowing of the lumen of the trachea or collapse of the trachea
This pathology has many causes – from a congenital predisposition to an acute allergic reaction. It causes a violation of the animal’s respiratory ability – breaths become short and unproductive, alternating with coughing. This provokes the development of general respiratory failure and a blue tongue.
Violation of the integrity of the respiratory tract
Injury to the trachea, larynx, lungs, neoplasms can lead to the manifestation of cyanosis of the tongue. By itself, an injury to the airways or lung tissue implies a violation of the dog’s ability to perform the normal act of inhalation and exhalation.
Insufficiency of respiratory muscles
Breathing is carried out due to the work of a number of respiratory muscles. In case of excessive relaxation of the skeletal muscles, disturbances in the functioning of nerve fibers or the center of respiration that sends impulses, oxygen starvation occurs, which is manifested by the cyanosis of the tongue.
Accumulation of air or fluid in the chest
The air or fluid in the chest does not allow the lungs to properly expand and fill with blood, which in itself prevents the blood from being saturated with oxygen. The result is oxygen starvation.

Pulmonary edema of any origin
The fluid filling the lungs disrupts their functioning, and, accordingly, causes a number of symptoms of oxygen starvation. Including the dog’s tongue turns blue.
Heart pathology
Various pathologies according to the type of disruption of the valve system, the presence of congenital anomalies, inflammation of the heart muscle, a tumor process, heart parasites – all this disrupts the throughput system of the heart. There is stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation, which prevents the normal saturation of blood in the lungs with oxygen.
Elongation of the veil of the palate – brachycephalic syndrome
This syndrome is typical for short-faced dogs – pugs, French and English bulldogs, etc. One of its signs is a thickening, elongation of the palatine curtain. This soft structure blocks the larynx and prevents the dog from taking a normal breath. During periods of exacerbation of respiratory failure, it can thicken so much that it does not allow the animal to take a breath at all. In this regard, manifestations of respiratory failure can be observed.
Bronchitis
An allergic reaction, an autoimmune process (excessively increased immunity), viral diseases, fungal infections of the lower respiratory tract cause spasm of the bronchial tissue. It is characterized by respiratory failure and the blue color of the tongue in the dog.
Eating pigmented foods
Some products and substances contain a pigment that can color the skin and oral mucosa. In particular, the tongue of a dog can become blue, brown, purple, violet. These include blueberries, mulberries, beets, activated charcoal.

Concomitant symptoms
With bronchitis, tracheal collapse, brachycephalic syndrome, injuries, the following may additionally be observed: coughing, coughing up clots of mucus or blood, reverse sneezing syndrome.
For pulmonary edema, prolonged oxygen starvation, a tense posture of the sphinx is characteristic, in which the animal lies on its stomach, its sides become sunken. The dog makes considerable efforts to perform the act of inhalation. She may also experience a decrease in body temperature.
With all types of oxygen starvation, there are: mixed type shortness of breath (both on inhalation and exhalation), cyanotic visible mucous membranes (oral mucosa, tongue, conjunctiva of the eye), unpigmented nasal mirror and skin, frequent shallow breathing.
In false cyanosis, the tongue gradually loses its strange coloration after washing the mouth with water or contact with other food.
Diagnostics
For any type of pathology, the following will be initially prescribed:
X-ray diagnostics of the chest and neck. It is performed in straight and two side laying – right and left.
Chest ultrasound – short T-Fast protocol to exclude or confirm acute respiratory or cardiogenic (extreme left ventricular failure) diseases
General clinical and biochemical blood tests
If there is fluid in the chest, a cytological (microscopic examination of one type of cell) and biochemical examination of the fluid is additionally performed.
If there is a suspicion of a neoplasm in the chest or in the upper respiratory tract, the following is prescribed:
Computed tomography of the chest
Histological (analysis of the structure of cells and tissues) and cytological examination of the formation, selected during a diagnostic thoracotomy (examination of the chest cavity) or endoscopic examination
If a diaphragmatic hernia is suspected, an X-ray examination with contrast (using a contrast agent) will be required.
In case of pulmonary edema, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound and ECG of the heart. This is necessary to confirm or exclude the cardiogenic origin of this pathology.
Bronchitis, asthma, tracheal collapse require bronchoalveolar lavage. During this procedure, a sterile saline solution is introduced into the lumen of the respiratory tract of a sedated (immobilized) animal, which is then withdrawn back. This liquid is sent for a comprehensive examination: PCR for respiratory infections, cytological examination, seeding to detect sensitivity to antibiotics.
Also, with these diseases, tracheo- and bronchoscopy is prescribed – an endoscopic examination of the respiratory tract.

Treatment
Therapeutic measures are provided only after the stabilization of the animal’s condition and the clarification of the primary diagnostic data – X-ray, ultrasound, blood tests.
Primary therapy for any disease is aimed at stabilizing the condition of the animal. It includes:
Oxygen therapy is a method that helps to increase the amount of oxygen in the air inhaled by animals.
Calming therapy. It is often necessary to take sedative (sedative) drugs such as tranquilizers / anticonvulsants (trazadone, gabapentin, vet-calm) to even out breathing
Control of temperature and pressure, glucose levels, as well as their correction if necessary.
Free fluid or air in the chest requires immediate removal. To do this, the hair is cut off, the surface of the skin is processed, and by puncturing the soft tissues in the intercostal space, a needle is inserted into the chest, through which air or liquid is removed with syringes, negative pressure is created.
If necessary, active drainage is installed – a permanently installed tube. A pear is attached to it, forcing pressure and constantly contributing to the removal of air or fluid from the chest.
In the case of active loss of protein in the breast fluid, it may be necessary to replenish its level by artificially injecting intravenous pure albumin, plasma, or blood from another animal.
In case of blood loss, serious damage, tumor processes, it is necessary:
blood transfusion under the supervision of a doctor strictly in a veterinary clinic
surgical intervention – removal of formations, surgical treatment of injuries, diaphragmatic hernia, etc.
installation of a tracheostomy – a tube that forms the airway through the trachea. It is used for significant injuries of the larynx, neck, head.
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema requires diuretic therapy with various drugs (Furosemide, Torasemide, Upkard, Veroshpiron and others), as well as the use of drugs that correct blood pressure (Dopamine, Dobutamine). Another doctor may prescribe Vetmedin to stimulate cardiac output.
Tracheal collapse, bronchitis, bronchopneumonia require hormonal therapy in the form of inhalation or oral administration (by mouth) of Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Budesonide, bronchodilators (Salbutamol) or antibacterial drugs (Baytril).
First Aid
Unfortunately, it is impossible to provide high-quality first aid to a pet with a blue or already burgundy tongue at home. A blue tongue in a dog that is also breathing heavily is a phenomenon, as a rule, an emergency. Therefore, if such a change is detected in combination with heavy breathing, lethargy or excessive excitability, it is necessary to immediately transport the animal to the clinic for examination and first aid. During transportation, it is important to put the pet in a comfortable position – on the stomach. It should also be provided with plenty of freely flowing air or oxygen (oxygen cartridges can be used).

Prevention
Annual clinical examination allows you to identify most of the diseases, deterioration, up to an emergency. Being under the supervision of a specialized medical doctor, it will be possible to prevent pulmonary edema, bronchial asthma, etc.
The appearance of brachycephalic syndrome can be prevented by timely rhinoplasty in a short-faced dog. The operation is best done at an early age. Injuries, allergic reactions, neurological disorders cannot be predicted. By themselves, these conditions require the immediate intervention of a veterinarian.
Blue tongue in dogs: summary
The cyanosis of the tongue or oral mucosa does not always indicate the presence of diseases in the animal. Some breeds have a blue tongue naturally or acquire it by eating coloring foods.
With cyanosis, the pathological blue of the tongue indicates a lack of oxygen in the body of the animal and a supersaturation with carbon dioxide – it suffocates.
The main reasons why a dog may have a blue tongue are: tracheal collapse, trauma, insufficiency of respiratory muscles, accumulation of fluid or air in the chest, pulmonary edema, heart disease, elongation of the palatine curtain, bronchitis or bronchopneumonia.
The main diagnostics include: x-ray, chest ultrasound, heart ultrasound, ECG, tracheo- and bronchoscopy, etc.
The treatment of this condition depends on the diagnosis. The urgency of the condition unites all diseases – immediate medical intervention and stabilization in a hospital are required.
First aid at home for a dog with a burgundy or bluish tongue is not possible. The owner needs to immediately transport the pet to the veterinary clinic.
The main prevention of this condition is the annual medical examination and observation of an animal with chronic diseases by a veterinarian.
Answers to frequently asked questions
February 13 2022
Updated: February 17, 2022