The dog’s eyes fester – why and how to treat?
Contents
Why does a dog’s eyes fester – 10 reasons
Most often, discharge from the eyes of a dog is purulent. It is important to understand that this is only a symptom of the underlying disease that needs to be identified and cured. Let’s take a look at the most common reasons.
Conjunctivitis
The conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that covers the inner surface of the eyelid. It contains a lot of cells responsible for immunity, therefore, with any changes in the eyes – the ingress of bacteria, viruses, parasites, the conjunctiva reacts sharply, swells and turns red. She also begins to actively secrete mucus, with which dead cells are utilized, which is why we see pus from the dog’s eyes. Inflammation of the conjunctiva is called conjunctivitis and has many causes, and treatment in each case is different. The most common conjunctivitis in dogs is bacterial.
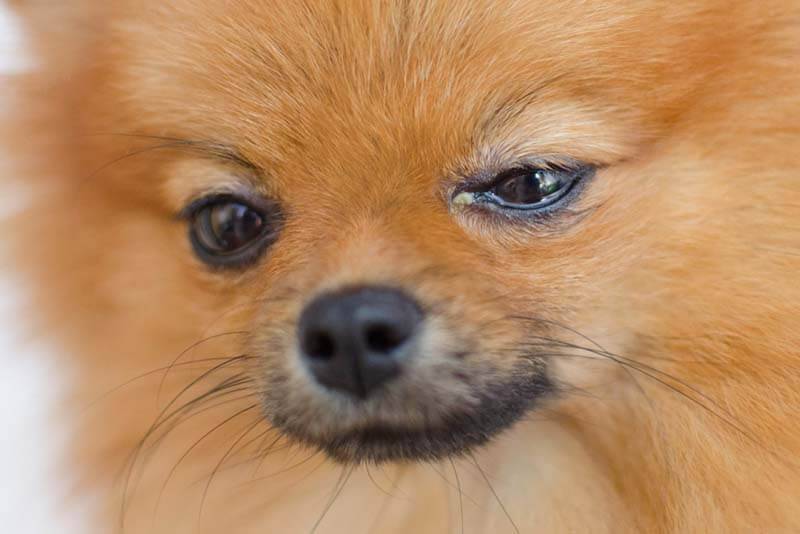

Blepharitis
This is a condition in which the outer part of the eyelid – the skin and edges – becomes inflamed. The most common cause of blepharitis is allergies. The disease can affect one or both eyes, accompanied by acute swelling, redness of the eyelids, itching of the skin and copious mucous secretions. In a dog, pus is released from the eyes, ulcers appear on the skin of the eyelids.
Inversion of the eyelids
With this pathology, the edge of the eyelid turns towards the eyeball (cornea), hair, eyelashes. Part of the eyelid, constantly in contact with the structures of the eye, injures them, causes irritation and inflammation. As a result, corneal ulcers can form, a bacterial infection joins, and abundant discharge from the eyes appears. Such breeds of dogs as Shar Pei, Mastiff, Chow Chow, Bulldog, Pug, Chihuahua, Caucasian Shepherd Dogs, Asians are predisposed to inversion of the eyelids.
Foreign body of the conjunctiva
As a rule, in the presence of foreign bodies in a dog, one eye fester. A foreign object, getting into the eye, causes a sharp inflammation, irritation of the conjunctiva, pain and other unpleasant sensations. The eye tries to protect itself and begins to actively secrete mucus in order to push out the foreign body.
Chronic ulcer of the cornea
Normally, the cornea is thin, transparent and shiny. When the upper layer is traumatized, a defect occurs, and the cornea breaks, forming an ulcer. The local immunity of the eye begins to actively heal the ulcer – to secrete a lot of mucus, tears, the animal cannot open its eyes. It becomes vulnerable to infections, purulent discharges are formed.
Dystrichia and ectopic eyelashes
Dogs, like humans, have eyelashes on their lower and upper eyelids. They can grow incorrectly – on the inside of the eyelid (ectopic eyelashes) or on the edge of the eyelid, turning towards the cornea of the eye (districhia) as they grow. Pathological eyelash growth is a hereditary pathology that occurs in Shih Tzu, Pekingese, English Bulldogs, Cocker Spaniels, Dachshunds, Spitz, Yorkshire Terriers, Samoyeds. Single soft eyelashes do not cause any particular complaints in the pet and are more common in young dogs. So, the fact that the puppy’s eye is festering becomes known by chance, only during an ophthalmological examination.
Pannus shepherd dog
Chronic inflammation of the cornea and conjunctiva due to genetics is called pannus. In this disease, the body perceives the cells of the cornea as foreign, and tries to reject them. German Shepherds are considered the main carrier of the disease, but the disease also occurs in other breeds of dogs and mestizos. The provoking factor of exacerbation of the disease is ultraviolet radiation. Against the background of an increased immune response, a concomitant disease occurs – plasmatic conjunctivitis with abundant purulent discharge from the eyes.
Eye neoplasms
Eye tumors can be primary or metastatic, benign and malignant, located inside the eye, on the eyelids and external structures of the eyeball. There is no age or breed predisposition. Any neoplasm changes the normal anatomical structure of the eye and interferes with its work. In this regard, often accompanying symptoms are discharge from the eyes.
Prolapse of the lacrimal gland
Dogs normally have an extra eyelid in the inner corner of the eye, and an extra lacrimal gland is located on its surface. The lacrimal gland of the third eyelid may change its normal position and turn out of the eye. It looks like a tight red ball in the inner corner of the eye. Most often, young dog breeds suffer from this: Beagle, Cocker Spaniel, French Bulldog, Chihuahua, Cane Corso, Mastiff, Mastiff, Labrador. The lacrimal gland becomes inflamed, reddens, tear exchange is disturbed, and the puppy’s eyes begin to fester, and if left untreated, dry eye syndrome develops.
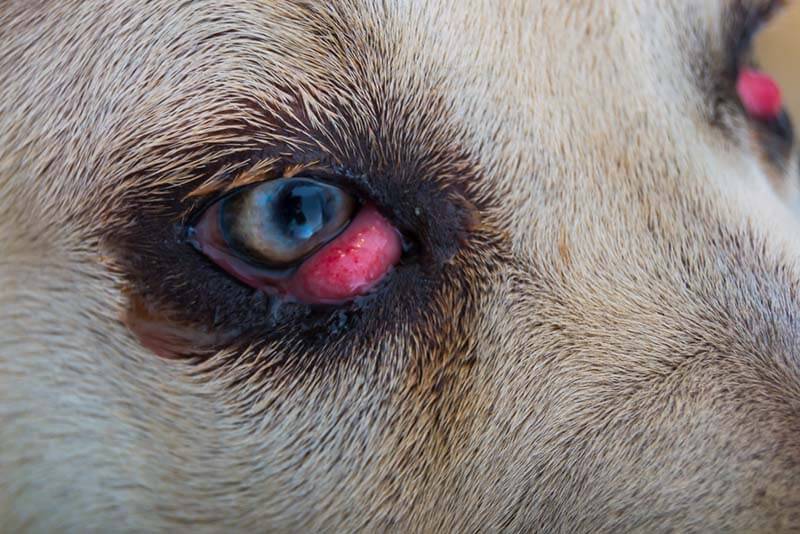
Eversion of the cartilage of the third eyelid
The third eyelid maintains its position, thanks to the dense cartilage in the center. If its part, facing the eyeball, grows faster than the front, cartilage collapses, and the eyelid turns outward. Cartilage collapse leads to a violation of the act of blinking and the development of inflammation. Most often found in large breeds – Weimaraner, St. Bernard, Newfoundland, Great Dane, Kurzhaar, Cane Corso, Bernese Sinnenhund.
Concomitant symptoms
In addition to secretions of a different nature, diseases are accompanied by other symptoms. In addition to obvious visual changes, with prolapse of the lacrimal gland, cartilage fracture or eye neoplasms, common accompanying symptoms develop.
Edema of the eyelids occurs due to itching, irritation of the skin with accumulated secretions.
Redness of the conjunctiva or skin of the eyelids. Any inflammation is an influx of blood to the site of penetration of bacteria, as a result, the mucous membranes and skin change color and turn red.
Blepharospasm – This is a condition in which the dog blinks heavily or almost does not open its eyes. This is a protective reaction of the eye to pain, burning and itching.
Epiphora – increased tear secretion, the hair around the eyes is wet and changes color.
Photophobia – the dog hides in dark places, covers his eyes with his paw, refuses to go outside.
Hair loss on eyelids. With an abundant accumulation of secretions, the hair constantly gets wet, and the skin becomes inflamed, as a result of which bald patches appear.
Narrowing of the palpebral fissure. Occurs due to swelling and redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes.
The general condition of the dog is changing, she sleep a lot, appetite and activityb also may be significantly reduced. With a long course of the disease, it may increase temperature.
If left untreated for an extended period, the dog may go blind. Without timely assistance, pannus shepherds, corneal ulcers, dystrichia and ectopic eyelashes, torsion of the eyelids, prolapse of the lacrimal gland and neoplasms inevitably lead to blindness.
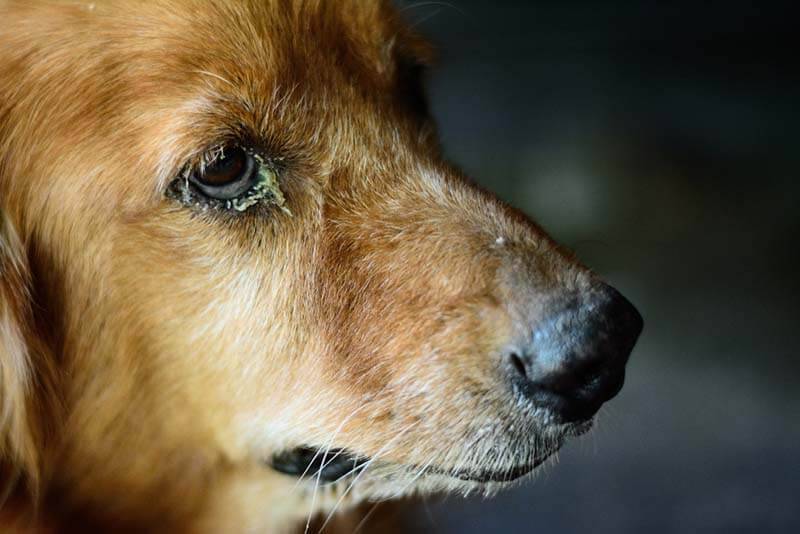

What to do if the dog’s eyes fester?
There are many causes of discharge from the eyes of a dog, and they are all very different. The treatment of each of the diseases is also radically different. In some cases, only washings, ointments, drops are enough, and somewhere surgical intervention is necessary. In most cases, you can not do without contacting a veterinarian, but first aid can be provided at home.
How to treat festering eyes in a dog?
Take a close look at your dog’s eye. Determine if external structures are changed, foreign objects, roughness on the cornea are not visible. In the presence of foreign bodies, try to remove them with abundant washing or a soft cotton swab.
Soak and remove all crusts and dirt. For processing, you can use clean warm water, it is safe if it gets into the eyes. If there are a lot of crusts and it is difficult to soak them, a mucolytic solution, such as ACC, can be used. Dissolve one tablet in a glass of water, moisten a gauze swab and wet the discharge and hair around the eyes with plenty of it. You can also wash the conjunctiva, the inside of the eyelid with this solution. The solution is safe for eye contact.
Rinse your eyes until all secretions are completely removed, then wipe dry with lint-free wipes or paper handkerchiefs.
Wear an anti-scratch collar and repeat rinsing as your eyes get dirty.
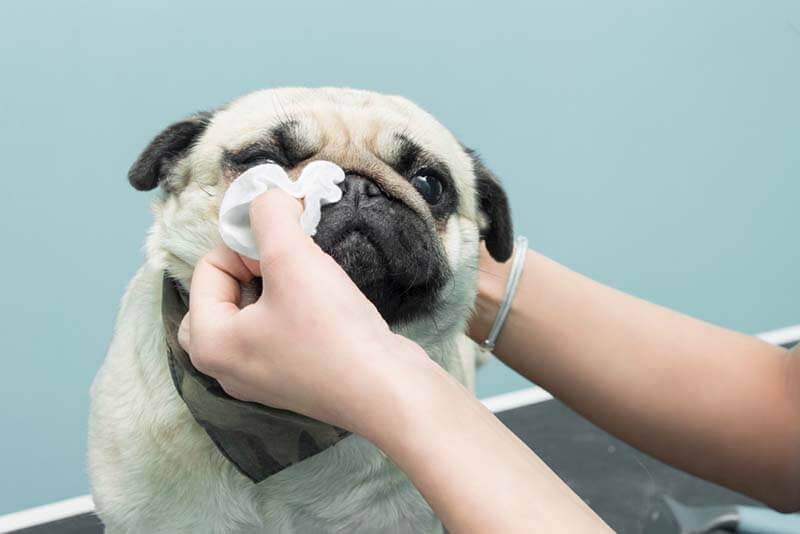
What can not be done?
It is not recommended to use chlorhexidine, potassium permanganate, furatsilin for washing; if they get into the eyes, they can cause burns. Also, ready-made veterinary lotions can be used for treatments, herbal decoctions and teas cannot be used. The presence of herbal particles can cause an additional allergic reaction and aggravate the condition of the eye.
In no case do not use drugs that contain hormonal components – dexamethasone, prednisone.
Avoid warm-ups. The influx of heat will increase inflammation and worsen the condition of the dog.
Do not use antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription, especially if the disease has been ongoing for a long time and you have already tried several drugs. It is important to contact the veterinary clinic with a true clinical picture even before the use of antibacterial drugs.
Treatment
After contacting the clinic, the doctor will examine the pet and determine why the dog’s eyes fester, and also recommend how and with what to treat it.
Contrary to popular belief, eye drops rarely completely clear pus when a dog develops conjunctival inflammation. Drops wash the eyes and only wash off the discharge, and ointments must be used for treatment. To relieve inflammation during the development of conjunctivitis, blepharitis, antibiotic ointments are needed: Floxal ointment, Tetracycline eye ointment. They should be applied 2-3 times a day for at least two weeks. Often, antibiotics are prescribed orally in a minimal dose, for example, Sinulox.
However, with the development of a corneal ulcer, drops are needed, they penetrate well through the mucous membrane and help healing. Treatment will also require moisturizers – Systane ultra, Oftalik, Korgergel, and antibiotics – drops of Tobrex, Floksal, Tsiprovet. They need to drip at least four times a day.
Do not forget about hygiene and rinse your eyes before each instillation of drugs.
Shepherd pannus, on the contrary, requires the use of drugs that suppress the immune system. In veterinary practice, Optimmun and local hormonal preparations are used. When outdoors, your dog should wear UV protection goggles. The therapy is lifelong.
Pathologies such as prolapse of the lacrimal gland, cartilage rupture, inversion of the eyelids, eyelashes, eye neoplasms are treated only surgically.
We recommend that you consult your veterinarian for the use of all of these drugs!
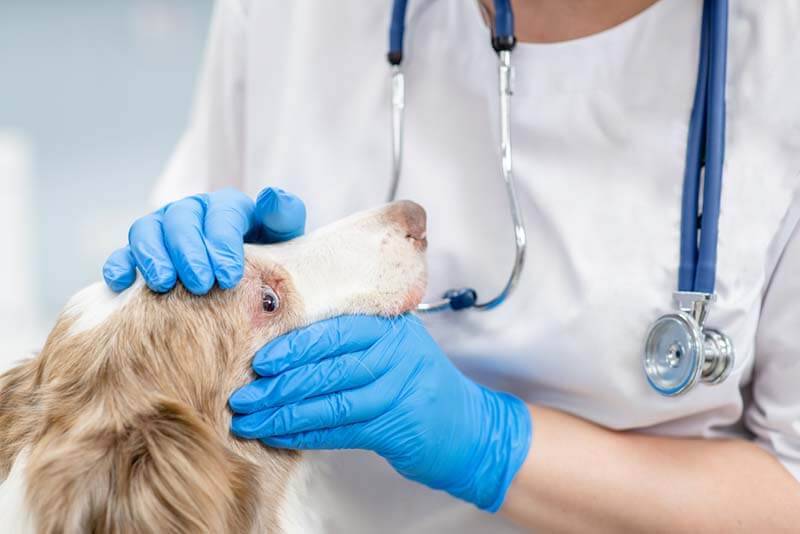
Prevention
To avoid inflammation, regularly carry out eye hygiene – after walking, playing or contact with other dogs.
Follow the rules of zoohygiene – regular treatment for parasites, vaccination, full feeding and grooming.
Before you take a puppy, find out about his parents, whether they were ill with breed diseases, whether operations were performed.
Get regular checkups with your veterinarian. Pathologies such as inversion of the eyelids, eyelashes and pathologies of the third eyelid, the doctor will notice at the reception in the early stages, which will quickly correct the situation.
Eye Pus in Dogs: Essentials
examine the dog, determine the possible cause of the discharge;
perform hygiene and clean the eyes of all secretions;
if you see a clear pathology – for example, a foreign body, try to remove it;
if the dog’s eye is festering, and you cannot determine the cause, the doctor should prescribe treatment, try to show the pet to a specialist as soon as possible;
protect your eyes from additional trauma by wearing a collar.
Answers to frequently asked questions