Dog abscess

Contents
Causes of abscesses
An abscess in a dog can occur for several reasons:
trauma due to which bacteria penetrate into damaged tissues. An abscess occurs at the site of an injury to the neck, head, back, and other places;
injections can also cause inflammation. A dog may develop an abscess after an injection if the rules of antisepsis or formulation of the drug are not followed. More often, after injections, owners find abscesses on the hind leg or between the shoulder blades in the dog;
suppuration of large hematomas. Usually, suppuration occurs if the hematoma affects a large number of soft tissues and lymphatic vessels. The site of inflammation depends on the location of the hematoma;
the penetration of bacteria into the lymph and the transfer of pathogenic microflora through the lymphatic vessels. Abscesses occur in the place of a large accumulation of blood vessels, it can be the armpits, groin, eyelids, or even the roots of the teeth;
the development of inflammatory processes within the body can cause internal abscesses. For example, due to pneumonia, they can appear in the lungs, due to mastitis in bitches – in the mammary glands, and so on;
foreign bodies. Any foreign object that should not be inside the body of the animal, the body will try to destroy – it encapsulates (hides) it and develops an abscess inside the cavity.
Concomitant symptoms
Symptoms will depend on the type of inflammation and its location.
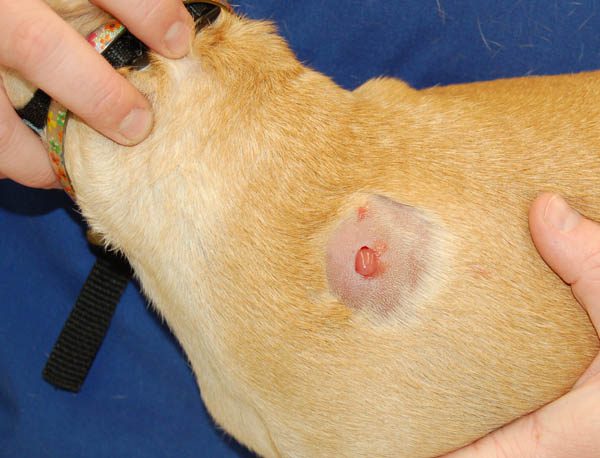
With the development of an acute abscess, the body temperature rises, extensive swelling occurs quite quickly at the site of accumulation of pus, it becomes hot and very painful. Further, the swelling is formed into a dense sphere with clear boundaries, with palpation, fluid is felt inside. After a few days, the skin becomes thinner and torn, pus flows out of the cavity. At the same time, the pet eats little, sleeps and drinks a lot, and does not allow touching the sore spot.
If the inflammation is chronic, then the general condition of the animal does not change, the temperature does not rise, the dog leads a normal life. The swelling grows very slowly, does not become hot. Sometimes its shape does not have a clear outline, and the abscess spreads to neighboring soft tissues. The skin changes color – it becomes darker, hair falls out at the site of inflammation.
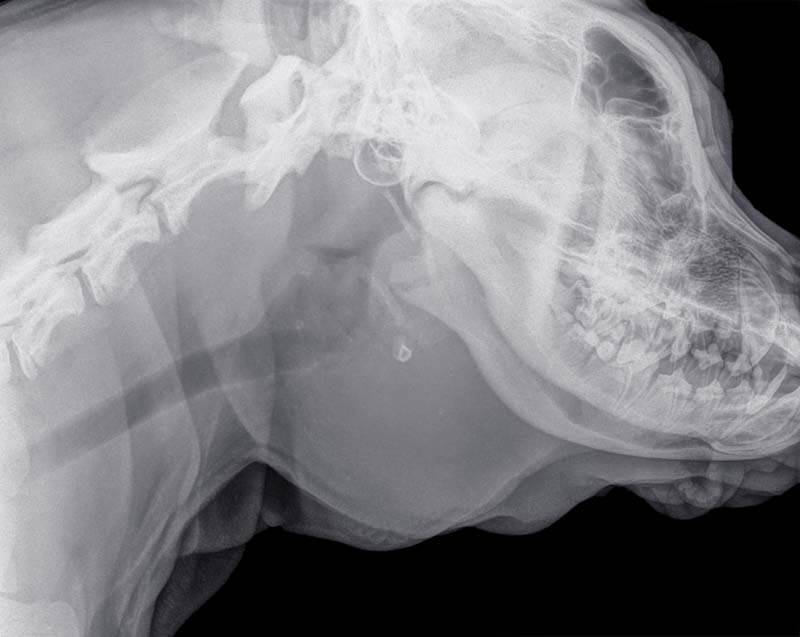
Also, the symptoms will depend on the location of the abscess. For example, with the development of an odontogenic abscess (inflammation of the roots of the teeth), an asymmetry of the pet’s muzzle, a decrease in appetite, and bloody saliva are found. Further, a lump with purulent contents is formed on the face next to the diseased tooth. With an abscess on the paw, the animal will limp, with the formation of inflammation on the liver, symptoms of liver pathology appear, and on the heart – heart failure.
Diagnostics
As a rule, an external abscess in a dog is not difficult to diagnose. On visual examination, swelling is visible, with palpation of the formation, fluctuation is felt (fluid inside the cavity with elastic walls). In this place, the skin changes color and hair falls out.
If the abscess is deep, then ultrasound and computed tomography are used as diagnostics. Thanks to a visual inspection, you can detect the localization of inflammation and its size. Next, the cavity is punctured (pierced) and determine what is inside it. The puncture is carried out in a clinic, observing the rules of antiseptics.
As an additional diagnostic, it is necessary to take blood tests to assess the degree of inflammation and its effect on the work of other organs.
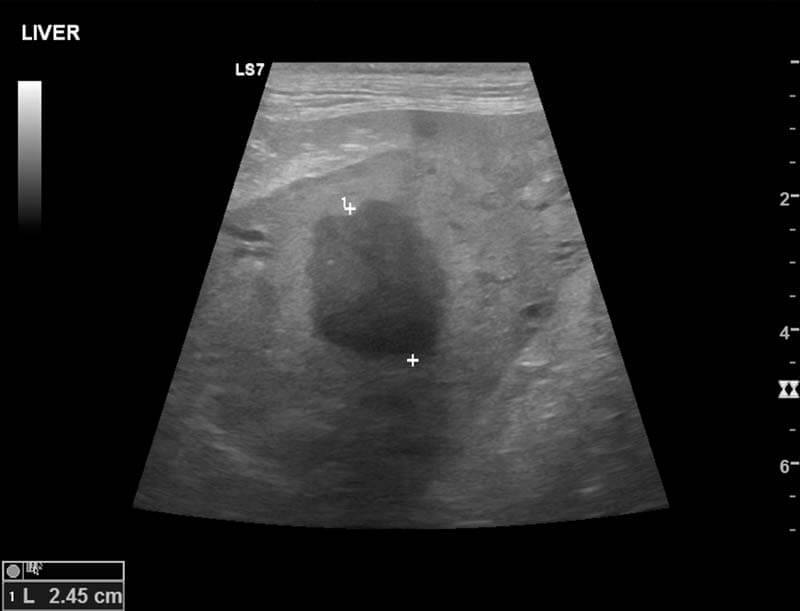
Treating an abscess in a dog
The treatment for an abscess in dogs is to create a constant flow of pus from the cavity and clean it, as well as control the bacteria that cause inflammation.
When an external abscess is detected, the doctor performs small incisions at two points – the lowest and the highest. Drainage tubes are inserted inside, removed through incisions, fixed and sanitized (cleaned) the cavity. Drainage and sanitation (cleansing) is carried out until pus forms. As soon as it dries, the drainage is removed and surface treatments are carried out until complete healing.
If an abscess forms inside the body, then a full-fledged surgical operation is required. Having determined its localization, the surgeon completely removes the capsule with pus and prescribes therapy to relieve inflammation.
To control the bacteria that cause abscess, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed – Synulox, Enroxil, Cephalen and others.
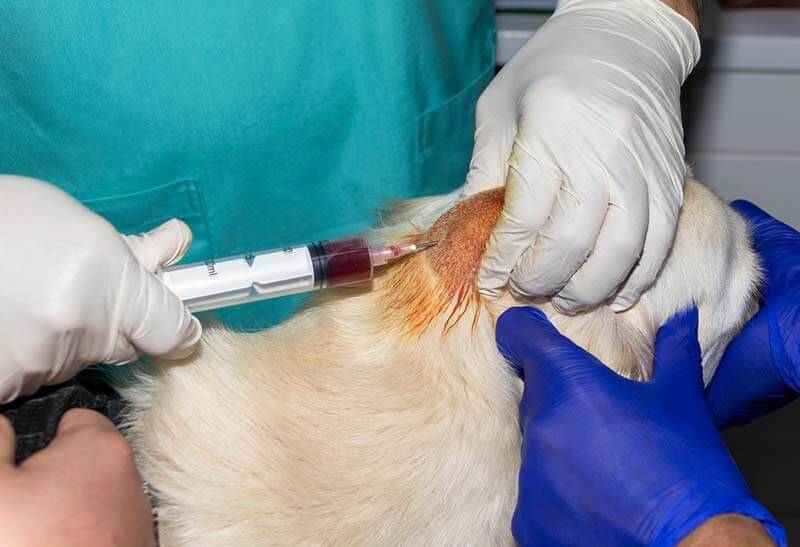
First aid
If you find an already open purulent wound in a dog, then it can be washed and protected from additional trauma.
For disinfection, use Chlorhexidine or Miramistin. Rinse the cavity, wound and area around it with a large amount of solution. Use gauze pads for processing. Then, inside the cavity and on top, apply an antibiotic ointment – Levomekol or Levosin. Protect the wound from licking and scratching by wearing a protective collar around the animal’s neck.
Do not apply tight bandages; oxygen must enter the cavity.
Do not open or squeeze out the abscess yourself. Incorrect opening of the cavity is likely to aggravate the condition – pus can enter the blood or healthy soft tissues, causing sepsis and fatal consequences. Be sure to contact your veterinarian, he will tell you in detail how to treat an abscess in a dog and perform a stripping.
Prevention
Protecting a pet from purulent wounds is not easy, but there are still some preventive measures.
After walking, inspect the dog, wash its paws thoroughly with water and soap. Eliminate self-walking and skirmishes with other pets.
After active play with other animals, carefully treat all scratches and wounds with Chlorhexidine solution. Rinse not only the surface of the coat, but also the skin so that the dog’s wound does not fester.
Observe preventive measures, feeding and hygiene standards.
Get vaccinated, dewormed, and oral cleaned annually. At home, you need to brush your teeth daily with a paste and brush, you should also use sprays – veterinary drugs that help in the fight against tartar.
Do not allow your pet to chew on bones, sticks and foreign objects.
Visit the veterinarian regularly and undergo medical examinations – be sure to take blood tests and do an ultrasound.
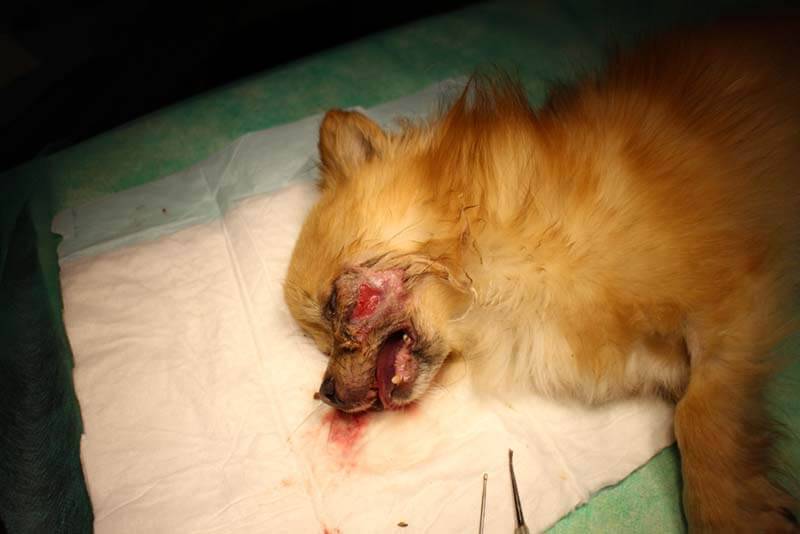
Abscess in dogs: summary
An abscess is a pathological process, as a result of which a limited cavity with pus and elastic walls is formed.
Inflammation can be on any part of the dog’s body – on the skin, muscles, mucous membranes and internal organs.
The causes of an abscess are foreign agents (substances) that enter the body from the environment after bites, scratches and other injuries due to lack of hygiene and improper injections.
Inflammation often causes general malaise – fever and pain.
Treatment should be carried out in a clinic, it requires the removal of pus from the cavity and the appointment of antibiotics.
Answers to frequently asked questions