DCMP in dogs is dilated cardiomyopathy

Contents
About DCM in dogs
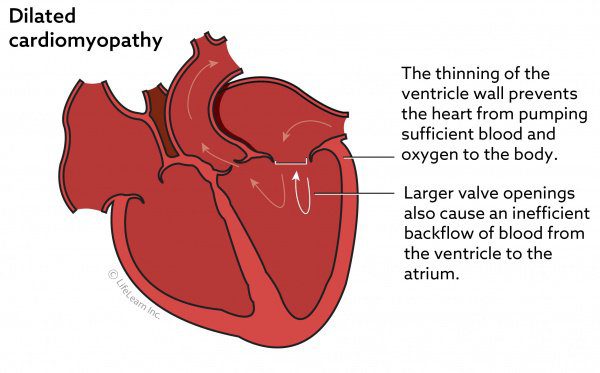
The left side of the heart is most often affected in dogs with DCM, although there are cases of damage to the right or both sides at the same time. The disease is characterized by thinning of the heart muscle, due to which the heart cannot effectively perform its contractile function. Subsequently, there is stagnation of blood in the heart, and it increases in size. Thus, congestive heart failure (CHF) occurs, and then
arrhythmiasViolation of the frequency and sequence of heartbeats, sudden death.
This pathology can be characterized by a latent course for a long period: the animal does not have any clinical symptoms, and the disease can be detected only during a cardiac examination.
The prognosis for dogs with this condition varies by breed and by condition at the time of admission. Patients with CHF usually have a worse prognosis than those who do not have it at the time of the visit to the veterinary clinic. This cardiomyopathy is rarely reversible, and patients usually have it for life.

Causes of the disease
DCM in dogs can be primary or secondary.
The primary form is associated with heredity, that is, a mutation of a gene occurs, which is subsequently transmitted to offspring and causes damage.
myocardiumMuscular tissue of the cardiac type.
The secondary form, which is also called the phenotype of dilated cardiomyopathy in dogs, occurs as a result of various factors: infectious diseases, long-term primary heart rhythm disturbance, exposure to certain drugs, nutritional causes (deficiency of L-carnitine or taurine), endocrine diseases (thyroid disease) . The causes described will cause symptoms and changes in the heart similar to the primary form.

Predisposition of breeds to DCMP
Most often, DCMP develops in such breeds: Dobermans, Great Danes, Irish Wolfhounds, Boxers, Newfoundlands, Dalmatians, St. Bernards, Caucasian Shepherd Dogs, Labradors, English Bulldogs, Cocker Spaniels and others. But the disease is not limited to specific breeds. As mentioned above, it is typical for all large and giant breeds of dogs. It was also found that in males, pathology is more common than in females.

Symptoms
As a rule, clinical signs appear in the late stages of the disease, when structural changes in the myocardium lead to dysfunction of the heart, and all the adaptive mechanisms of the body are disrupted. Signs of DCM in dogs vary by stage of the disease, and they may appear suddenly and progress rapidly. Affected animals usually observe: shortness of breath, cough, decreased physical activity, fainting, decreased appetite, weight loss,
ascitesFluid in the abdomen.
Diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy
The main task of diagnostics is to identify the disease at an early stage and remove the animal from breeding. It all starts with the collection of an anamnesis, examination of the animal, during which
auscultationListening to the chest with a phonendoscope. It allows you to detect murmurs in the heart, a violation of the heart rhythm.
To assess the general condition, a hematological and biochemical blood test is performed, including electrolytes, thyroid hormones, as well as such an important marker of myocardial damage – troponin I.
For breeds such as Dobermans, Irish Wolfhounds and Boxers, there are genetic tests to identify the genes that lead to this problem.
Chest X-ray is useful for determining conditions such as venous congestion, pulmonary edema, pleural effusion, and for assessing the size of the heart.
Ultrasound examination of the heart provides the most accurate determination of the size of each section of the heart, wall thickness, assessment of contractile function.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) can measure your heart rate and diagnose any abnormal rhythms. However, Holter monitoring is the gold standard in diagnosing arrhythmias. Like humans, dogs are given a portable device that they wear for 24 hours. Throughout this period, the heart rate is recorded.
Treatment of DCM in dogs
Treatment for canine dilated cardiomyopathy depends on the stage of the disease and the severity.
hemodynamic disordersCirculatory disorders.
There are several groups of drugs used in this pathology. The main ones are:
Cardiotonic drugs. Pimobendan is the main representative of this group. It increases the force of contraction of the ventricular myocardium and has a vasodilating effect.
Diuretic drugs that have a diuretic effect. They are used to control the formation of congestion in blood vessels and free fluid in natural cavities – chest, pericardial, abdominal.
Antiarrhythmic drugs. Since arrhythmias often accompany heart disease, causing tachycardia, fainting, sudden death, these drugs can stop them.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. ACE inhibitors are used to regulate circulation and blood pressure.
Auxiliary agents: therapeutic diet for animals with cardiac diseases, nutritional supplements (taurine, omega 3 fatty acids, L-carnitine).

Prevention
Large and giant breeds of dogs, especially those with DCM as a genetic disease, should undergo an annual cardiac examination, echocardiography, ECG, and, if necessary, Holter monitoring.
For Dobermans, Boxers, Irish Wolfhounds, genetic tests are available to determine the presence of the disease and promptly remove the animal from breeding.
Every pet needs a balanced diet. Do not forget about planned treatments for endo- and ectoparasites and vaccination.

Home
DCM in dogs is a disease in which the heart muscle becomes thin and weak.
Pathology is most common in large and giant breeds of dogs.
For some breeds, this cardiomyopathy is a genetic disease. But it can also occur due to other factors (infections, endocrine diseases, etc.).
One of the main diagnostic methods are echocardiography and the method of daily monitoring according to Holter.
If a disease is detected in breeds with a genetic predisposition, it is necessary to remove the animal from breeding.
The disease can be asymptomatic for a long time. The most common symptoms include: cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, fainting. For treatment, several groups of drugs are used depending on the clinical manifestations, the stage of the disease: cardiotonic drugs, diuretics, antiarrhythmic drugs, etc.
Sources:
Illarionova V. “Criteria for the diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy in dogs”, Zooinform veterinary medicine, 2016. URL: https://zooinform.ru/vete/articles/kriterii_diagnostiki_dilatatsionnoj_kardiomiopatii_sobak/
Liera R. «Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Dogs», 2021 URL: https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/dilated-cardiomyopathy-dcm-in-dogs—indepth
Prosek R. «Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Dogs (DCM)», 2020 URL: https://www.vetspecialists.com/vet-blog-landing/animal-health-articles/2020/04/14/dilated-cardiomyopathy-in-dogs
Kimberly J. F., Lisa M. F., John E. R., Suzanne M. C., Megan S. D., Emily T. K., Vicky K. Y. «Retrospective study of dilated cardiomyopathy in dogs», Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 2020 URL: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jvim.15972