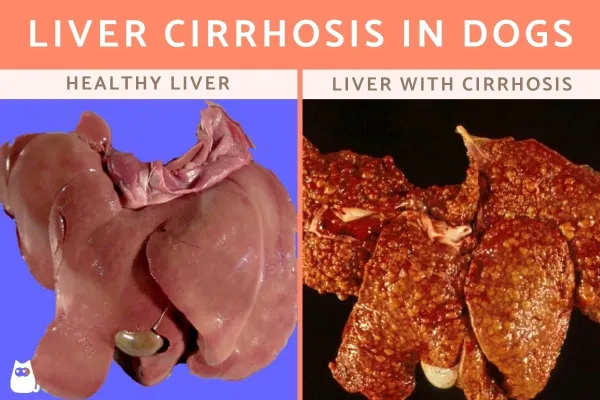
Cirrhosis of the liver in dogs

Contents
Cirrhosis in Dogs: Essentials
- Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease with no cure.
- It is more common in older dogs than in younger ones.
- The causes of the development of the disease are extremely diverse.
- The main symptoms of liver cirrhosis in dogs include decreased appetite, vomiting, discoloration of feces and urine.

Causes of cirrhosis
The reasons for the development of cirrhotic changes are varied. For the occurrence of any changes in the tissues of the liver, the action of a damaging factor is necessary. In dogs, these can be various toxins, drugs, infectious and invasive processes. In response to the action of the damaging factor, the death of hepatocytes – liver cells occurs. The body tries to resist this process and activates compensatory processes, the place of the dead cells must be taken by something. Connective tissue cells grow faster than hepatocytes, and the dog develops liver fibrosis. Then the process of angiogenesis begins – the formation of new blood vessels. New vessels are surrounded by connective tissue, which reduces their volume. The vessels form a new network, connecting the main vessels of the liver – the hepatic artery and the portal vein. But the new vasculature is able to pass a small volume of blood, and also maintains a higher pressure than should be normal. As a result, pressure begins to build up in the portal vein, leading to portal hypertension.
The main factors damaging the liver are as follows:
Medicinal products
Some drugs, when taken uncontrolled, can lead to serious changes in the liver. These drugs include phenobarbital, which is often used for convulsive syndrome in dogs. Glucocorticoid preparations in high doses and for a long course also lead to serious side effects, including liver disease. Some dogs are hypersensitive to the antiparasitic drug mebendazole (which is rarely found on the market lately), in high doses it will be extremely toxic. Antibiotics from the tetracycline group and some antifungal drugs (ketoconazole) can be extremely dangerous if used uncontrolled. Paracetamol, even in medium doses, can cause irreversible changes in the liver in dogs.
Toxins
Dogs are fond of chewing on various inedible objects. The ethylene glycol contained in antifreeze is sweet in taste, and dogs do not neglect to feast on it if left in their access. Chewing gums and toothpastes for humans contain xylitol, which is also toxic to animals. Eaten batteries begin to oxidize in the dog’s stomach and release heavy metals. Aflatoxins are secreted by many parasitic fungi (eg molds) and have a hepatotoxic effect. Fungicides, insecticides and some rodenticides are highly toxic when ingested.
Infections
The most common liver infection in dogs is leptospirosis. Leptospira are bacteria that penetrate the liver, kidneys, lungs and some other tissues of a living organism. Infection mainly occurs through infected water (most often in puddles) or after eating rodents that have died from the disease. Another disease is infectious hepatitis caused by adenovirus type 1. Recently, this disease is not very common and almost does not occur due to conscientious vaccination of domestic dogs.
Invasions
Parasites are relatively rare in the liver of dogs. A helminth that parasitizes directly in the liver (Opisthorchis felineus) causes opisthorchiasis. Infection occurs through eating infected untreated fish. Other helminths (toxocars, roundworms) are also able to migrate to the liver in the course of their life and lie there in the form of larvae.
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis in dogs
The clinical signs that occur with liver cirrhosis in dogs can be quite varied. Their severity will depend on the stage of the disease. The dog may become less mobile, get tired faster. Most of the day will sleep. Body weight will slowly decrease. Appetite is sluggish, and thirst can be both within the normal range and increased. Vomiting will occur periodically, vomiting of bile is possible. The chair will be unstable, diarrhea alternates with constipation. The color of urine may become darker, almost brown. Feces may, on the contrary, lose color and become gray or white. The skin and mucous membranes in some cases become icteric, that is, acquire a yellow tint. Due to hypertension in the portal vein of the liver, it is often possible to note an increase in the volume of the abdomen due to ascitic fluid in it.
Normally, the liver produces various factors of the blood coagulation system, including vitamin K. With cirrhosis, the production of these substances is reduced, bleeding can be observed: blood does not stop well at the site of injury, blood impurities appear in urine and feces, gums bleed, bruises appear on the body. In the extreme stages of cirrhosis, nervous phenomena can be found due to the development of hepatic encephalopathy. The pet has convulsions, tremors, impaired coordination. Possible death of the pet.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of cirrhosis is established in a complex way, that is, it is necessary to take into account the history of life and illness, clinical signs and data from visual and laboratory studies. It is necessary to remember whether the dog could have been poisoned by something, whether they gave her some medicines on her own. Also, the doctor will be helped by data on available vaccinations and treatments against parasites.
During the examination, the color of the mucous membranes, the rate of capillary filling, the degree of dehydration, pain and pathological changes in the abdomen, and body temperature are evaluated. General clinical and biochemical blood tests are taken. In a clinical blood test, anemia can be detected, the leukocyte formula is usually without significant changes. According to the biochemical blood test, an increase in liver enzymes and bilirubin is detected. In the extreme stage of cirrhosis, there may be no changes in the biochemical blood test, since the cells that produce these substances have completely died.
With a low level of blood albumin, there will often also be an effusion in the abdominal or chest cavity. In some cases, blood glucose and urea will be reduced. With an increase in the level of bile acids, the formation of secondary hepatic shunts can be suspected.
A blood test for leptospirosis by microagglutination is often recommended. To study for infectious hepatitis, the method of polymerase chain reaction or enzyme immunoassay is used. An ultrasound of the abdominal cavity with an emphasis on the liver area is mandatory. In the presence of effusion, fluid is taken for its study in order to exclude tumor and inflammatory processes.
The final diagnosis of cirrhosis in most cases can be made only with the help of histological examination.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis in dogs
If the dog has eaten a poisonous substance, you should contact the nearest clinic as soon as possible. In the clinic, it may be suggested to induce vomiting in order to quickly evacuate the toxin or gastric lavage. Droppers are prescribed to relieve intoxication. If the toxic substance is known, a suitable antidote can be used.
Treatment of infectious diseases consists in the introduction of antibacterial, antifungal and antiparasitic drugs. Sami cirrhotic changes in the liver, unfortunately, are irreversible. That part of the liver tissue, which was replaced by connective tissue, is no longer able to recover. Only symptomatic and supportive treatment of liver cirrhosis in dogs is used. Special therapeutic diets are prescribed for liver diseases. Vitamins such as vitamin B12, E and K may be added.
Choleretic drugs are prescribed, that is, choleretic drugs. Sometimes drugs from the group of hepatoprotectors are prescribed. Although these drugs do not belong to the database of evidence-based medicine, when using them, a positive effect can often be noted. These drugs include S-adenosylmethionine and milk thistle fruit extract.

Prevention
To prevent the development of liver diseases, including cirrhosis in dogs, it is necessary to follow the basic rules for keeping a pet. It is necessary to remove all toxic substances from the dog’s access. It is necessary to conduct an annual comprehensive vaccination, which includes protection against infectious hepatitis and several strains of leptospirosis. Preventive treatments for internal parasites are carried out at least four times a year for walking dogs and monthly for dogs that hunt or eat raw meat.
Annual medical examination helps to identify the disease in the early stages and take the necessary measures in time.
22 2021 June
Updated: 28 June 2021